Figure 3.
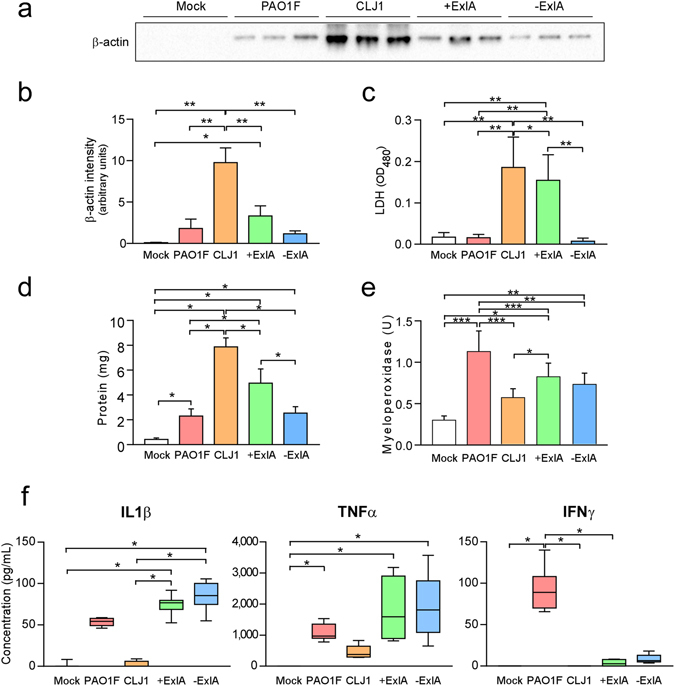
Intracellular proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines in broncho-alveolar lavages. BALs were sampled at 18 h.p.i. after pulmonary infection with PAO1F, CLJ1, +ExlA or −ExlA (5 × 106), or mock infection with PBS, and were centrifuged to separate the cellular pellet from the soluble proteins. (a) Western blot analysis of β-actin in 3 BAL supernatants per condition (representative of 6–8 BALs per condition) and (b) histogram of band intensities. Statistics: ANOVA, p < 0.001; Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: *p = 0.031, **p < 0.001. (c) LDH measurements in 6 BAL supernatants per condition. Statistics: ANOVA, p < 0.001; Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: *p = 0.028, **p < 0.001. (d) Total proteins in BAL supernatants (n = 6). Statistics: ANOVA, p < 0.001; Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: *p < 0.001. (e) Myeloperoxidase activity in BAL pellets (n = 6). Statistics: ANOVA, p < 0.001; Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: ***p < 0.001, **p = 0.003, *p < 0.05. (f) IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ concentrations were measured in BAL supernatants (n = 6–8). Statistics: Kruskal-Wallis’s test, p < 0.001; Dunn’s post-hoc test: *p < 0.05. IL-10, IL-17 and IL-12p70 dosages yielded negligible values for all strains (not shown).
