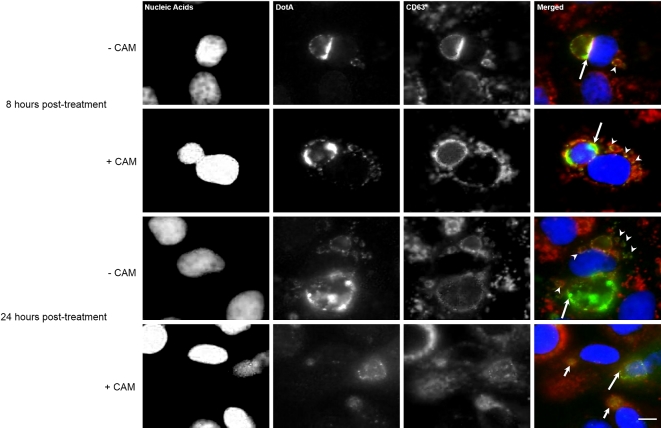
Figure 5.
DotA–host cell membrane association is dependent on bacterial protein synthesis. Representative monochrome and respective merged fluorescence micrographs of Vero cells infected with C. burnetii and either mock treated (–CAM) or treated with 10 μg/mL chloramphenicol (+CAM) at 72 hpi. Top group: Infected cells were fixed 8 h after the mock treatment and chloramphenicol treatment. Nucleic acids (blue), DotA (green) and CD63 (red) were fluorescently labeled. At 8 h post treatment (hpt), DotA is visible in the PV membrane (long arrows) and cytoplasmic vesicles (arrowheads) for the both the mock and chloramphenicol-treated cells. Bottom group: Infected cells were fixed 24 h after the mock treatment and chloramphenicol treatment. Nucleic acids (blue), DotA (green) and CD63 (red) were fluorescently labeled. By 24 hpi, the +CAM cells had DotA associated only with PVs that are considered spacious (long arrow) and absent from collapsed PVs (short arrows) and also is no longer observed within the host cell cytoplasm while in the –CAM cells had DotA present in the PV (long arrow) and the cytoplasmic vesicles (arrowheads). Scale bars equal 10 μm.