Figure 2.
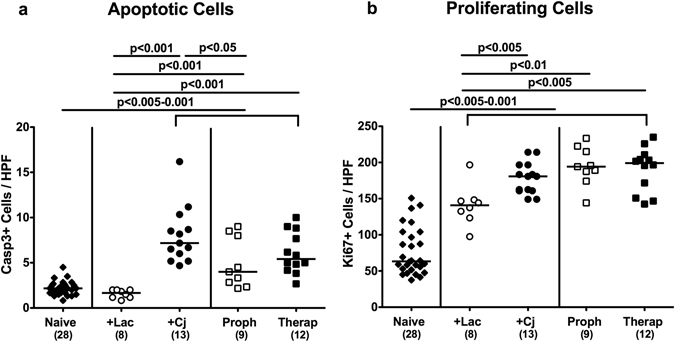
Apoptotic and proliferating cells in the colonic epithelium of C. jejuni strain 81–176 and/or L. johnsonii associated secondary abiotic mice. Secondary abiotic mice were perorally infected with C. jejuni strain 81–176 (Cj) and associated with L. johnsonii (Lac) either 14 days before (prophylactic regimen, Proph; white squares) or 7 days thereafter (therapeutic regimen, Therap; black squares) and compared to mono-associated mice (+Lac, white circles; +Cj, black circles). The average number of colonic (a) apoptotic cells (positive for caspase-3, Casp3) and (b) proliferating cells (positive for Ki67) from six high power fields (HPF, 400x magnification) per animal was determined microscopically in immunohistochemically stained colonic paraffin sections at days 21 or 28 following initial C. jejuni or L. johnsonii infection, respectively. Naive mice (black diamonds) served as uninfected controls. Medians (black bars), levels of significance (p-values) determined by one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey post-correction test for multiple comparisons and numbers of analyzed animals (in parentheses) are indicated. Data were pooled from three independent experiments.
