Figure 5.
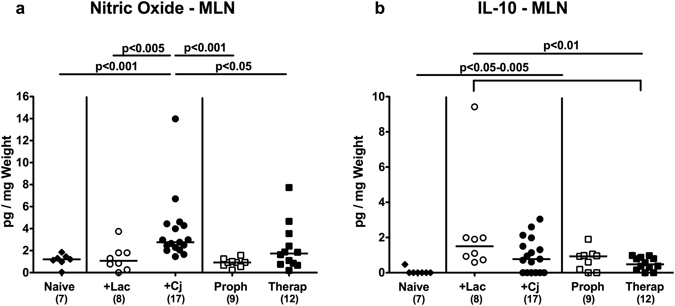
Secretion of pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators in mesenteric lymph nodes of C. jejuni strain 81–176 and/or L. johnsonii reassociated secondary abiotic mice. Secondary abiotic mice were perorally infected with C. jejuni strain 81–176 (Cj) and associated with L. johnsonii (Lac) either 14 days before (prophylactic regimen, Proph; white squares) or 7 days thereafter (therapeutic regimen, Therap; black squares) and compared to mono-associated mice (+Lac, white circles; +Cj, black circles). (a) Nitric oxide and (b) IL-10 concentrations were determined in ex vivo biopsies derived from mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) at days 21 or 28 following initial C. jejuni or L. johnsonii infection, respectively. Naive (N) mice (black diamonds) served as uninfected controls. Medians (black bars), level of significance (p-value) determined by one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey post-correction test for multiple comparisons and numbers of analyzed animals (in parentheses) are indicated. Data were pooled from three independent experiments.
