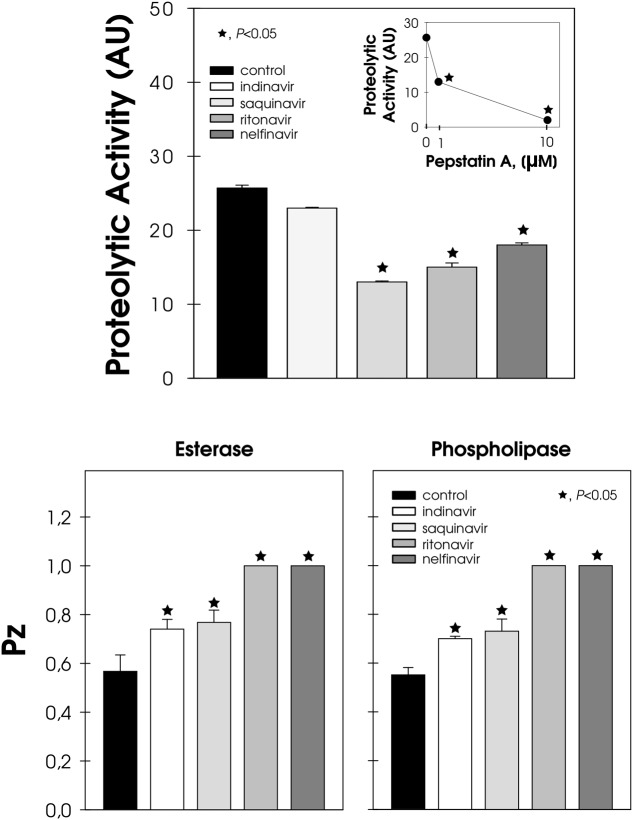
FIGURE 5.
Effect of HIV-PIs on the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes by F. pedrosoi conidial cells. Untreated (control) and HIV-PI-treated (100 μM for 24 h) conidial cells were washed and re-suspended in Czapek-Dox medium for an additional 2 h. After this period, the cell-free culture supernatants were submitted to a proteolytic activity assay. In addition, the supernatant obtained from the control cells was pre-incubated in either the absence or presence of pepstatin A (1 and 10 μM) and then checked for their ability to cleave BSA (inset graphic). The proteolytic activities were expressed as arbitrary units (AU). In parallel, conidia treated (or not) with HIV-PI were placed in the center of either Tween 80 or egg-yolk agar plates to detect esterase and phospholipase activities, respectively. The lipase activities were expressed as Pz and the values represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Symbols (★72) indicate the experimental systems considered statistically significant from the control (P < 0.05, Student’s t-test).