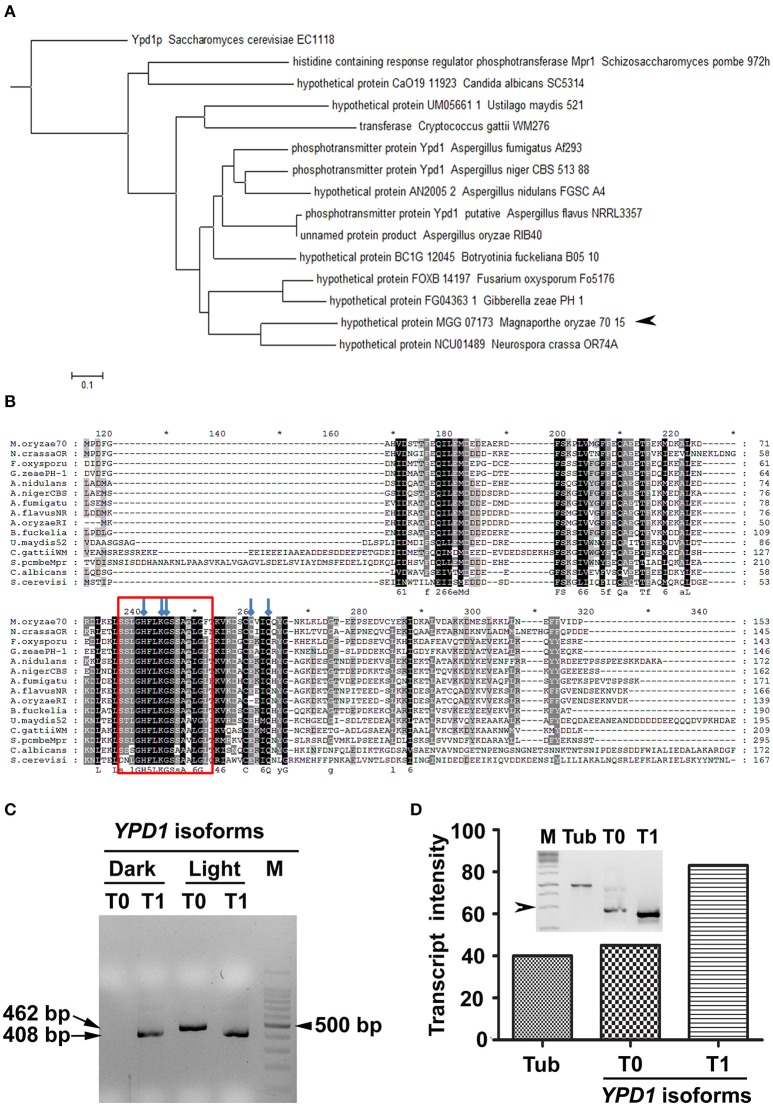
Figure 1.
Identification of Ypd1 and its gene isoforms in M. oryzae. (A) A dendrogram showing phylogenetic analysis of the Ypd1 sequences from various filamentous and non-filamentous fungi. Arrowhead denotes Ypd1 from M. oryzae. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of Ypd1 sequences from different fungi. The red box marks the highly conserved catalytic region in the Ypd1 sequence. Blue arrows show amino acids (H83, K86, G87, Q102, and Q105) crucial for functional folding of the protein. (C) Amplified cDNA products of the differentially accumulated YPD1 isoforms (T0 or T1) under different growth conditions (dark vs. light). Size of the cDNA or a fragment from the 100 bp DNA ladder (M) is mentioned. (D) Graphical and qualitative (inset) representation of the ratiometric analysis of the transcript levels of the YPD1 isoforms (T0 and T1) under photo-illumination, with respect to that of tubulin (Tub) as an internal control, in the WT M. oryzae. Arrowhead depicts 500 bp fragment from the 1 Kb DNA ladder (M). The asterisks denote 10-digit interval in the multiple sequence alignment.