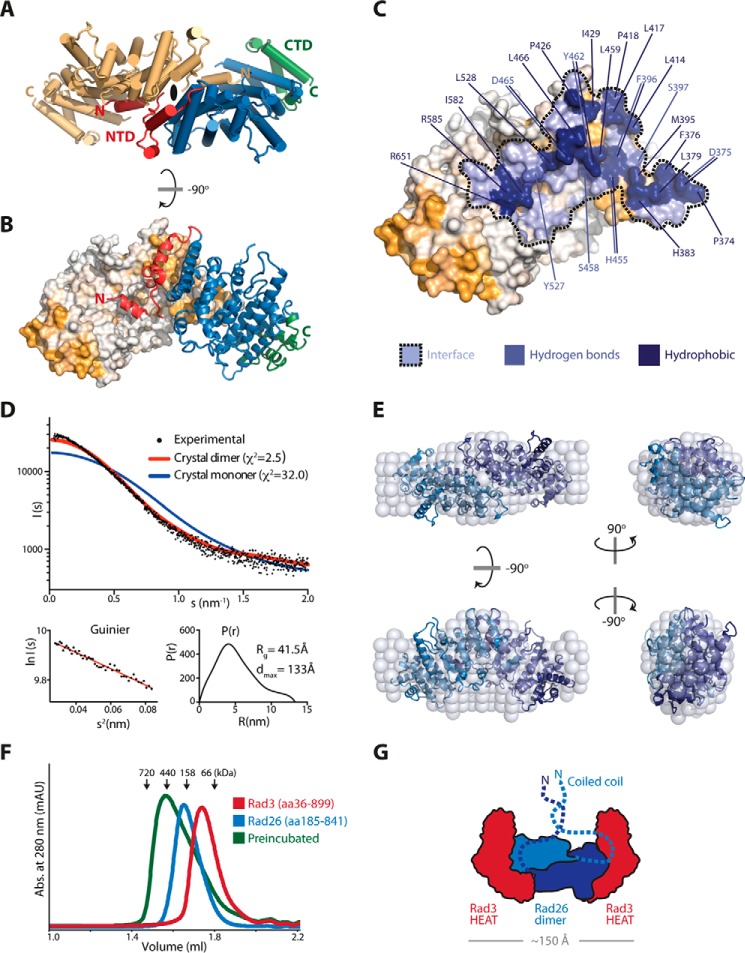
Figure 4.
Support for a dimeric Rad26. A, top view of the Rad26 dimer with one molecule colored in light orange, and the other molecule colored as in Fig. 1. The 2-fold symmetry axis is indicated at the dimer interface. B, side view of the Rad26 dimer showing the highly conserved NTD is the interface site between the two molecules. C, the footprint of the Rad26 dimer interface is in blue marked with a dotted line, and residues that contribute hydrogen bonds and strong hydrophobic interaction (above 0.44 kcal/mol) are indicated. D, CRYSOL fit of the theoretical scattering for the Rad26 crystal dimer (red) and monomer (blue) to the experimental scattering with the Guinier plot and the pair distance distribution P(r) below. E, low resolution ab initio DAMMIN model of Rad26 (spheres) with the Rad26 crystal dimer superimposed. F, analytic gel filtration of the Rad3-Rad26 complex absorbance (abs.). G, proposed model for the organization of the heterotetrameric Rad3-Rad26 complex.