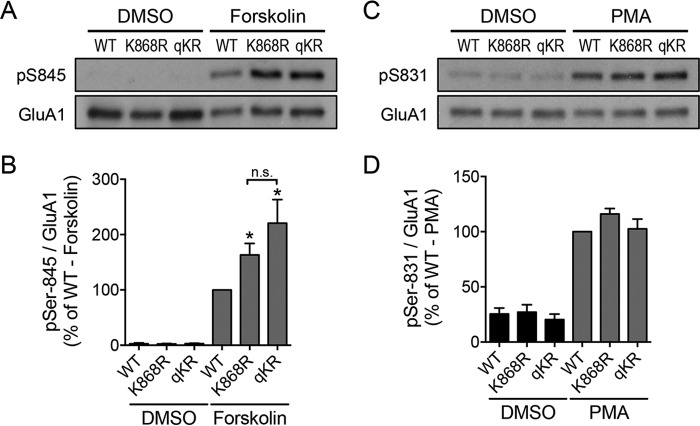
Figure 4.
Ubiquitination negatively regulates GluA1 phosphorylation at Ser-845. Cortical neurons were electroporated with pH-GluA1 constructs, either WT or ubiquitin-deficient mutants as indicated, prior to plating. qKR contains quadruple mutations of Lys-813, Lys-819, Lys-822, and Lys-868 in the GluA1 C-terminal tail into arginines. At DIV14, neurons were treated with 20 μm forskolin (A), 0.1 μm PMA (C), or DMSO for 10 min and immediately lysed with 1× SDS sample buffer. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis and probed with anti-GluA1 phospho-Ser-845, anti-GluA1 phospho-Ser-831, and anti-GluA1 antibodies. The effects of GluA1 ubiquitin-deficient mutants on the phosphorylation levels at Ser-845 (B) and Ser-831 (D) were quantified as phospho-/total receptor ratios and normalized to wild-type controls. Data represent the mean of five independent experiments (one-way ANOVA; *, p < 0.05; n.s., not significant; n = 12). Error bars represent S.E.