Figure 5.
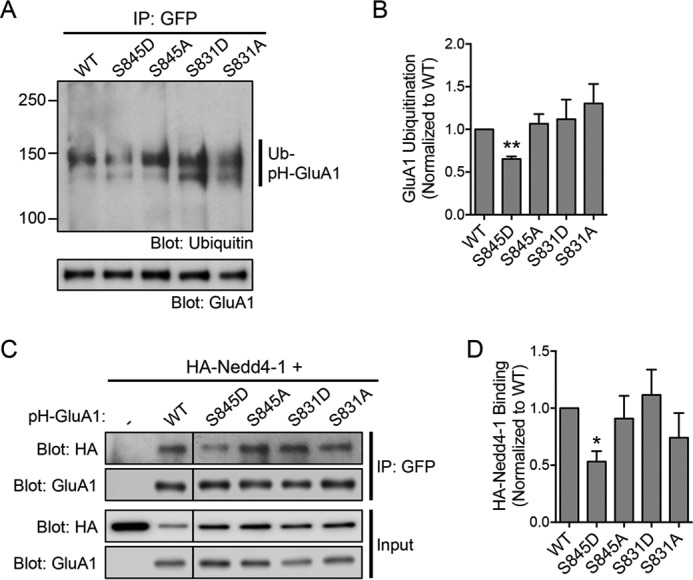
The S845D phosphomimetic mutant blocks GluA1 ubiquitination by reducing its interaction with Nedd4-1. A, cortical neurons were electroporated with pH-GluA1 constructs, either WT, phosphodeficient (alanine mutations), or phosphomimetic (aspartate mutations) as indicated, prior to plating. At DIV14, neurons were treated with 100 μm AMPA in the presence of 1 μm tetrodotoxin and 50 μm d-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid for 10 min and immediately lysed in 1% SDS. Diluted lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies (IP: GFP). Eluted proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis and probed with anti-ubiquitin (Ub) and anti-GluA1 antibodies. B, the effects of GluA1 phosphorylation mutants on agonist-induced ubiquitination were quantified and normalized to the wild-type control. Data are represented as the mean of three independent experiments (one-way ANOVA; **, p < 0.01; n = 4). C, HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-Nedd4-1 alone (−; lane 1) or together with pH-GluA1 constructs, either wild type, phosphodeficient (alanine mutations), or phosphomimetic (aspartate mutations) as indicated. Cells were lysed 48 h later and subjected to immunoprecipitation assays with anti-GFP antibodies (IP: GFP). Total cell lysates and eluted proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis and probed with anti-HA and anti-GluA1 antibodies. D, the effects of GluA1 phosphorylation mutants on HA-Nedd4-1 binding were quantified and normalized to the wild-type control. Data are represented as the mean of three independent experiments (one-way ANOVA; *, p < 0.05; n = 3). Error bars represent S.E.
