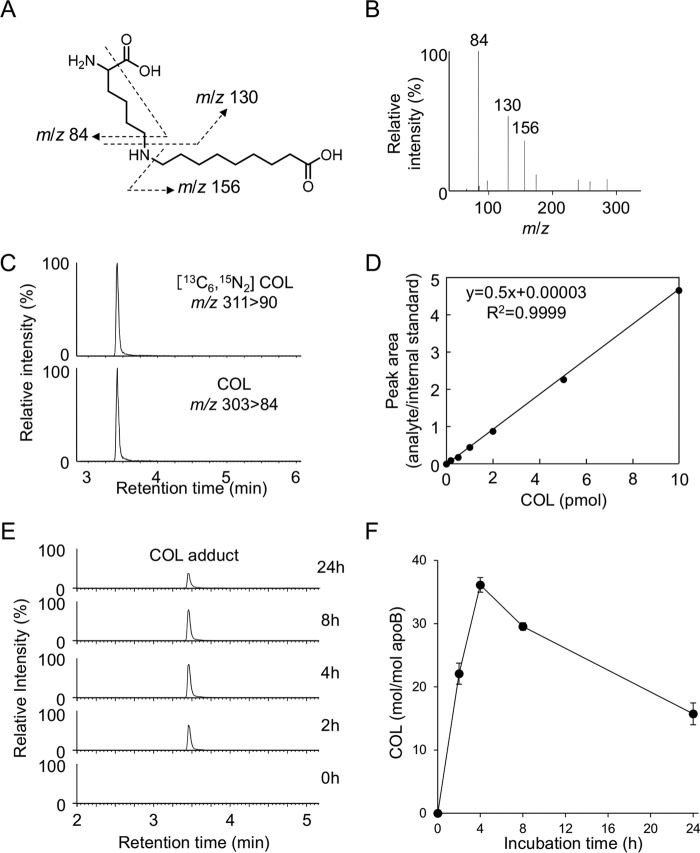
Figure 9.
Quantification of COL adduct in Cu2+-oxidized LDL. A and B, collision-induced dissociation of the [M + H]+ of COL adduct at the collision energy of 25 V. A, proposed structures of individual ions. C, LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of [13C6,15N3]COL adduct. Upper, SRM for [13C6,15N3]COL adduct (m/z 311 > 90); lower, SRM for COL adduct (m/z 303 84). D, calibration curves for COL adduct. E and F, time-dependent formation of COL adduct in the Cu2+-oxidized LDL. The LDLs were analyzed by LC-ESI-MS/MS in the SRM mode following NaBH4 reduction and acid hydrolysis.