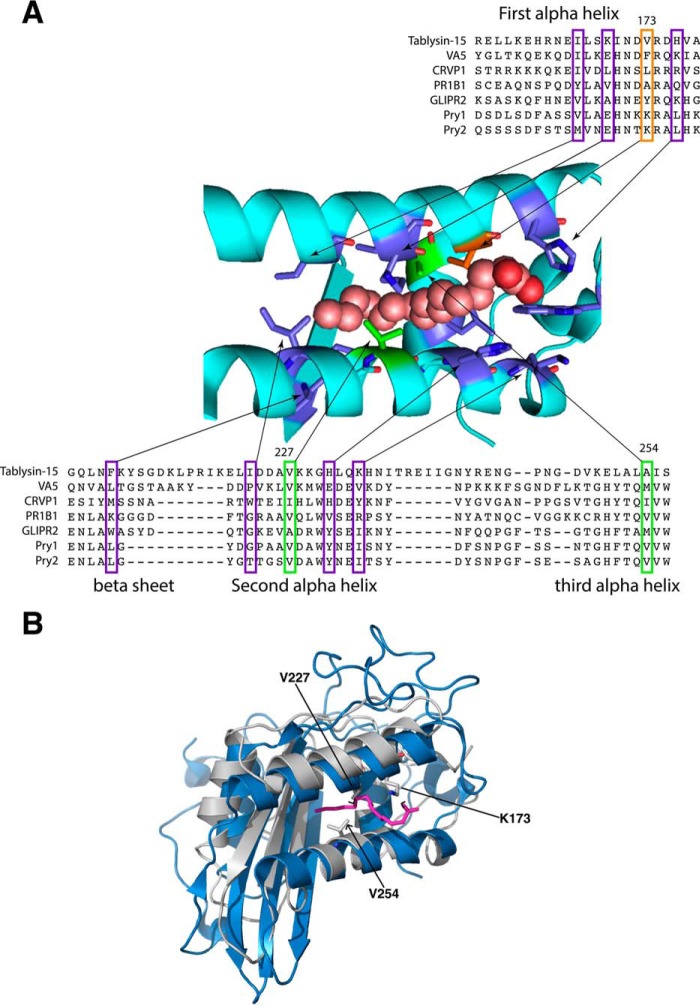
Figure 1.
The palmitate-binding site of tablysin-15 is conserved in yeast Pry1. A, a multiple sequence alignment limited to the residues important for palmitic acid binding of tablysin-15 with taxonomically diverse CAP family members is shown. Sequences from the following CAP family members with their UniProt identifier given in the parentheses were aligned: horsefly tablysin-15 (F8QQG5), wasp venom allergen 5 (VA5, Q05110), Naja atra natrin-1 (CRVP1, Q7T1K6), tomato PR1B1 (P04284), human GLIPR2/GAPR1 (Q9H4G4), yeast Pry1 (P47032), yeast Pry2 (P36110). Key residues shown in colors are those forming the fatty acid-binding site in tablysin (12). Shown in green and orange are those that were mutated. B, comparison of the structure of the fatty acid-binding pocket of tablysin-15 to that of yeast Pry1. The structures of the two proteins around the fatty acid-binding pocket are superimposed with tablysin-15 in blue and Pry1 in gray with the bound palmitic acid shown in magenta. Key residues lysine 173, valine 227, and valine 254 are indicated.