Figure 5.
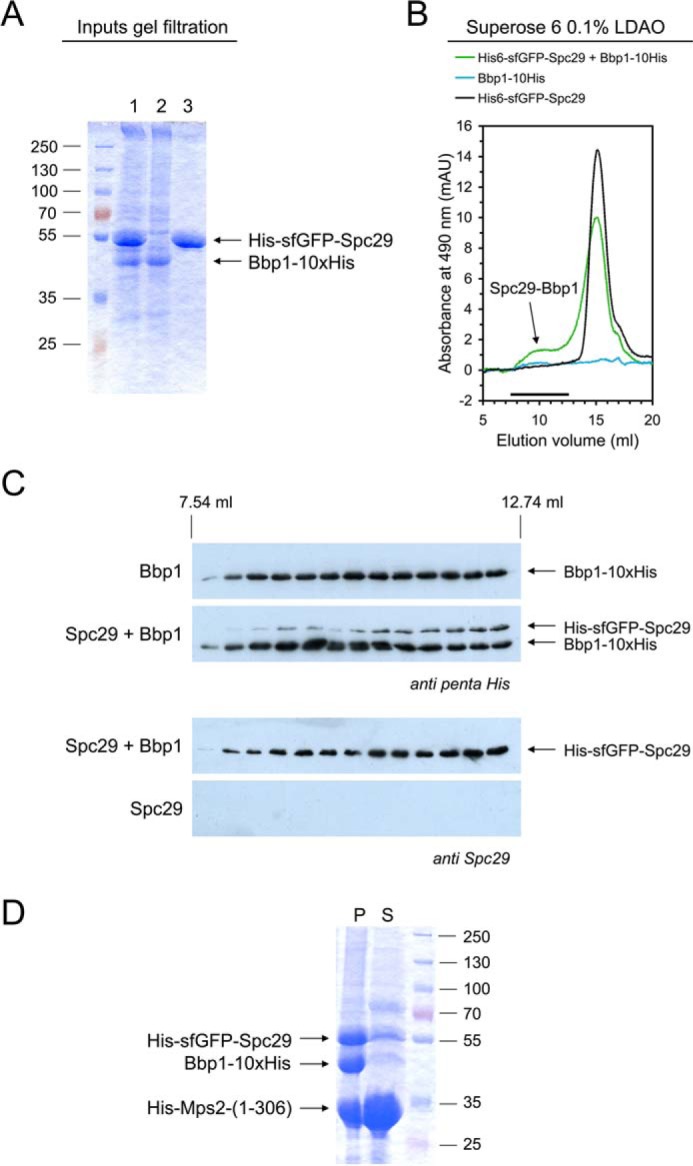
Reconstitution of Spc29-Bbp1 complexes. A and B, a molar excess of His-sfGFP-Spc29 was mixed with Bbp1-His10 in LDAO-containing buffer for 15 min at room temperature. The single Bbp1-His10 and His-sfGFP-Spc29 proteins were treated in the same way. Protein solutions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (1, His-sfGFP-Spc29 + Bbp1-His10; 2, Bbp1-His10; 3, His-sfGFP-Spc29) (A) and by gel filtration on a Superose 6 column following the absorbance at 490 nm (absorbance maximum of GFP proteins) (B). mAU, milliabsorbance units. An arrow indicates the Spc29-Bbp1 complex. The shoulder in the Spc29 chromatogram in presence of Bbp1 indicates Spc29 oligomerization. C, proteins eluted from the Superose 6 column were subjected to immunoblotting using anti-penta-His and anti-Spc29 antibodies, respectively. D, coprecipitation of the soluble N-terminal domain of Mps2 together with Spc29 and Bbp1. His-Mps2-(1–306) (in molar excess), Bbp1-His, and His-sfGFP-Spc29 co-precipitated at a low LDAO concentration (∼0.03%). The assay was centrifuged for 5 min at 20,000 × g and separated into pellet (P) and supernatant (S) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. The supernatant still contained soluble His-Mps2-(1–306) but only minor amounts of Spc29 and Bbp1.
