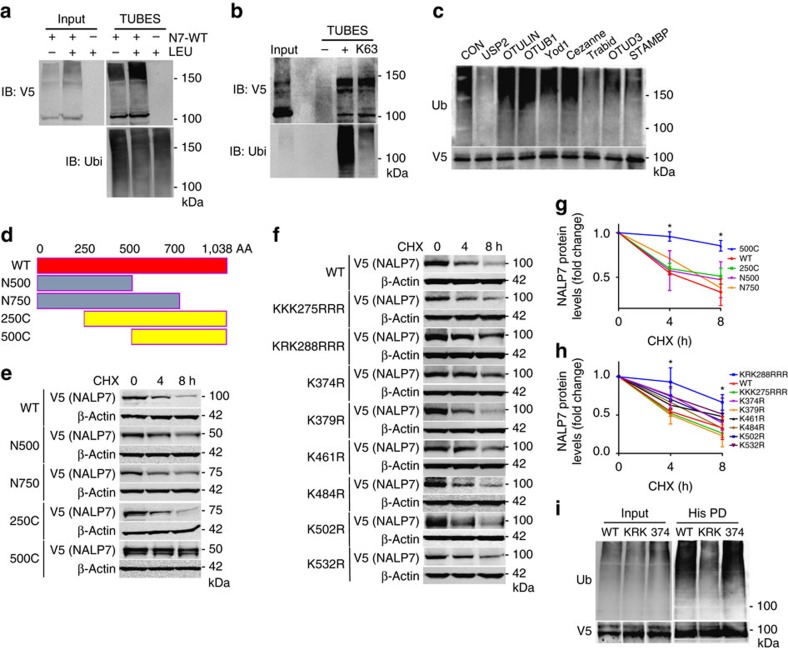
Figure 3. Identification of NALP7 ubiquitin acceptor sites.
(a) TUBEs pulldown of ubiquitinated NALP7-V5 from denatured Beas2B cell lysates increased with leupeptin (LEU) (50 μM) treatment compared to untreated control. (b) Ubiquitinated NALP7-V5 was identified by immunoblotting after pulldown with non-selective TUBEs reagent and anti-K63 TUBEs from denatured Beas2B cell lysates. (c) UbiCREST assay. Immunopurified Ub-NALP7-V5 abundance decreased when incubated at 37 °C for 30 min with purified, recombinant USP2, Trabid, OTUD3 and STAMBP, but not OTULIN, OTUB1, Yod1 or Cezanne in vitro. (d) Mapping of NALP7 using truncation mutants. (e) Half life analysis of transfected wild-type and truncation mutant NALP7-V5 and (f) transfected K→R point mutant NALP7-V5 in Beas2B cells. (g,h) Densitometric analysis of (g) NALP7 truncation mutant and (h) NALP7 K→R point mutant signal versus time, normalized to β-actin. Data shown as mean±s.d. (n=2). *P<0.05 compared to wild-type using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. (i) Immunopurified NALP7-V5 KRK288RRR (KRK) mutant showed decreased ubiquitination compared to wild-type or K374R mutant in Beas2B cells.