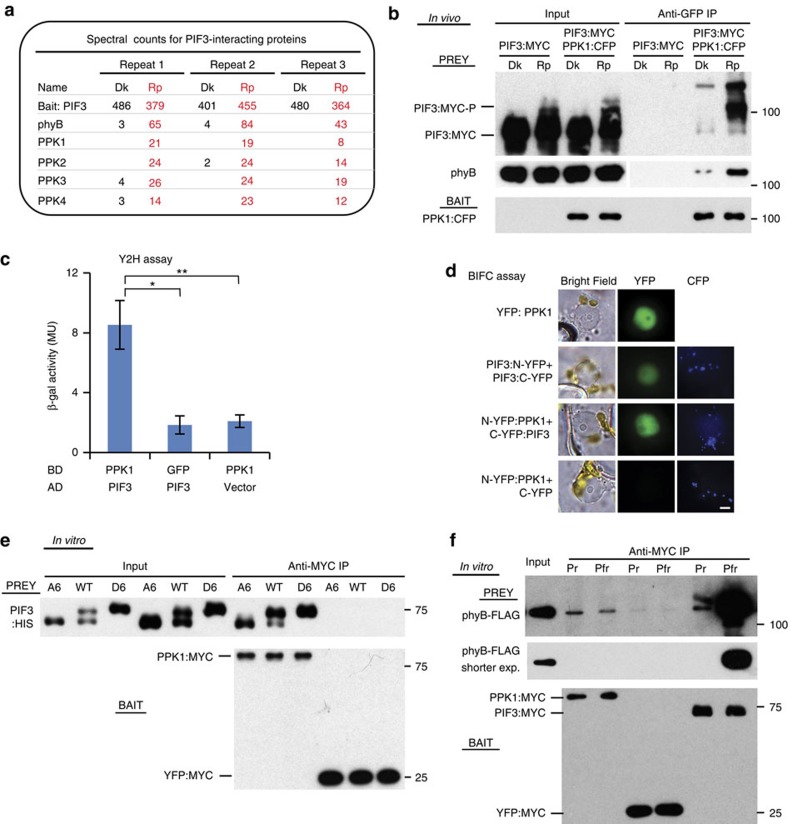
Figure 1. In vivo light promotes the interaction of PPKs with PIF3 and phyB.
(a) PIF3-interacting proteins detected by co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) from cell extracts and subsequent mass spectrometric analysis. Spectral counts from three biological replicates of dark (Dk)-grown and red-light-pulse (Rp)-treated seedlings, respectively. (b) In vivo light-induced interaction of PPK1 with PIF3 and phyB detected by co-IP and subsequent immunoblot analysis. Protein extracts from Dk- or Rp-treated seedlings of the indicated genotypes were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies, to pull down CFP-tagged PPK1 as bait, and the immunoblot was probed with either anti-MYC antibody (top, Prey), anti-phyB antibody (middle, Prey) or anti-GFP antibody (bottom, Bait) to detect PIF3:MYC, phyB and PPK1:CFP, respectively. (c) PIF3 and PPK1 interact in yeast-2-hybrid (Y2H) assays. LexA-DNA-binding-domain-fused PPK1 or GFP were used as bait, and B42 activation-domain-fused PIF3 or empty vector were used as prey in a standard Y2H configuration. Error bars represent standard error (s.e.) from three biological replicates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student's t-test). (d) PIF3 and PPK1 interact in transient-transfection, Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assays. Light-grown Nicotiana benthamiana leaves were transfected with the constructs indicated and then exposed to 10 min FR light and incubated in darkness for 72 h before microscopic analysis. Constructs used: YFP:PPK1, yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) fused to PPK1 protein; N-YFP and C-YFP, N- and C-terminal domains of split mVenus210 fluorescent protein, respectively, fused (or not) to PIF3 or PPK1 proteins. All split-Venus constructs also carried the mTq2 Golgi-localized marker as a positive control for transfection. Imaging configuration: Bright field, YFP emission filter; CFP (Cyan Fluorescent Protein) emission filter. Quantification of nuclei displaying split-Venus fluorescence shown in Supplementary Fig. 2a. Scale bar, 5μm. (e) Interaction of in vitro-synthesized recombinant PPK1 and PIF3 proteins detected by co-IP assays as described in b, except that the PPK1 bait was tagged with MYC (PPK1:MYC), and immunoprecipitated with anti-MYC antibodies, and the PIF3 prey was tagged with HIS (PIF3:HIS). YFP:MYC bait was used as a negative control. The immunoblot was probed with either anti-HIS antibody (top, Prey) or anti-MYC antibody (bottom, Bait). WT, wild-type PIF3 sequence; A6, PIF3 variant with phospho-dead mutations; D6, PIF3 variant with phosphomimic mutations4,17. (f) In vitro-synthesized, recombinant PPK1 and phyB interact as detected by co-IP assays as described in b, except that the PPK1 bait was tagged with MYC (PPK1:MYC) and immunoprecipitated with anti-MYC antibodies, and the phyB prey was tagged with FLAG (phyB:FLAG). PIF3:MYC was used as a positive-control bait for light-induced phyB activation and YFP:MYC as a negative control. The immunoblot was probed with either anti-FLAG antibody (top and middle, Prey), or anti-MYC antibody (bottom, Bait). Pfr and Pr, samples were irradiated with R light only, or R followed by FR, respectively, before immunoprecipitation.