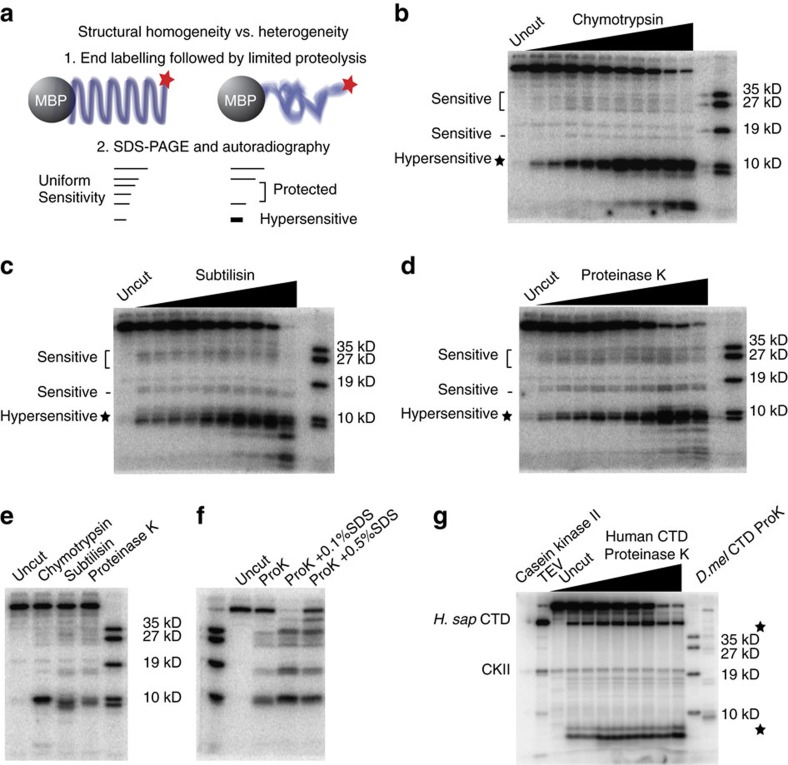
Figure 4. The CTD is structurally heterogeneous across its length.
(a) Experimental design: end-labelled MBP-D.melCTD is subject to limited proteolysis, SDS-PAGE, and autoradiography. A completely unstructured, or alternatively, a structurally repetitive CTD is predicted to generate a uniform pattern of proteolytic fragments. A structurally heterogeneous CTD is predicted to give rise to a non-uniform pattern. (b) Limited proteolysis with chymotrypsin generates a non-uniform pattern of CTD fragments, with a hypersensitive site in the distal CTD, a sensitive region in the proximal CTD, and a largely protease insensitive region in the central CTD that is cleaved at only one site. The right most lane contains radiolabelled CTD fusion proteins with the molecular weights designated on the right of the panel. (c,d) Limited proteolysis with subtilisin or proteinase K reveal similar sites of sensitivity and protection. (e) A direct comparison of proteolytic fragments generated by three proteases shows a similar by not identical pattern of proteolysis. (f) Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) alters the relative proteolytic sensitivity of the CTD to proteinase K, enhancing the sensitivity of the CTD at sites that generate bands near 35 kD and below 19 kD relative to the CTD ladder (0.1% SDS lane). 0.5% SDS renders the globular MBP portion of the fusion protein more susceptible to proteolysis, evidenced by the proteolytic fragment above the 35 kD CTD ladder band but below the intact fusion. (g) The human CTD is radiolabelled on the final acidic repeat by casein kinase II (CK2) (uncut lane). TEV cleavage to separate the human CTD from the MBP fusion demarcates the point below which protease sensitivity occurs in the CTD portion of the protein (TEV lane). Limited proteolysis with proteinase K reveals a distal hypersensitive site reminiscent of that observed in the Drosophila CTD (compare to D.melCTD ProK lane), a protease hypersensitive proximal site near MBP and a central region that is largely protease insensitive. Both the human and fly CTDs share distal protease hypersensitivity, proximal sensitivity that is localized to a discrete region in the human CTD, and a more central region of the CTD that is less protease sensitive.