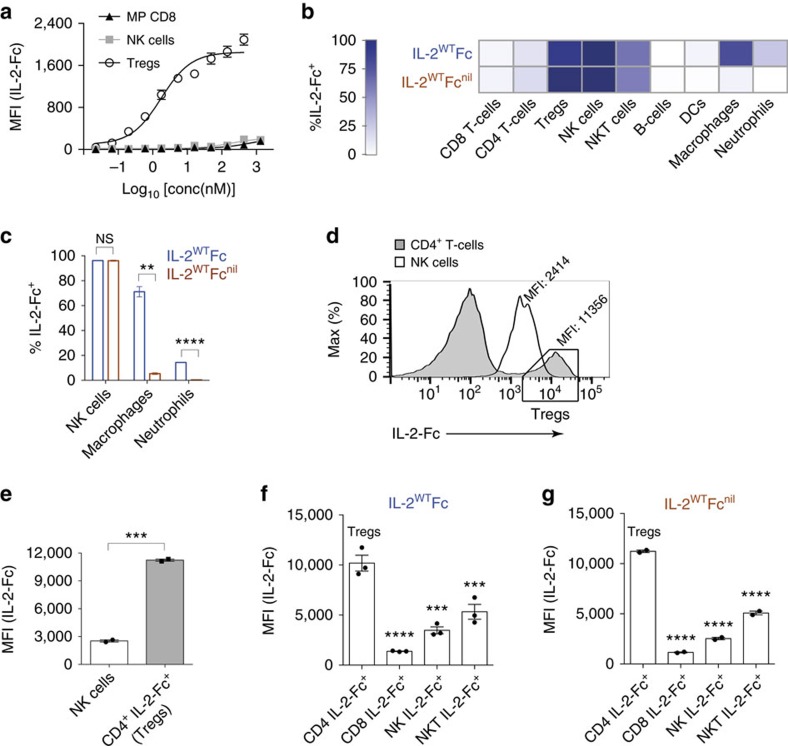
Figure 4. Depletive IL-2WTFc activity relies on high-affinity targeting of Tregs and interaction with myeloid effector subsets.
(a) Ex vivo flow cytometric detection of labelled IL-2WTFc on the surface of MP CD8, NK cell and Treg subsets after incubation with Fc-blocked FoxP3DTR/GFP splenocytes (n=2 technical replicates). (b–g) Cellular biodistribution profiles of fluorescently labelled IL-2WTFc and IL-2WTFcnil in the spleens of treated C56BL/6 mice as determined by flow cytometry 12 h post injection (16.8 μg IL-2-Fc i.p., n=2–3 mice per group). (b) Heat-map representation of the percentages of lymphoid and myeloid subsets bound by IL-2-Fc-fusion proteins (c) Abolition of FcγR binding causes a significant reduction in the percentages of macrophages (P=0.0041) and neutrophils (P<0.0001) bound by fluorescent IL-2-Fc, as determined by two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. (d) Representative histograms displaying the levels of IL-2WTFcnil present on CD4+ T-cells and NK cells after i.p. injection. Box indicates that the majority of CD4+ IL-2-Fc+ cells are Tregs, as previously shown in Supplementary Fig. 5C. (e) Quantification of d, showing significantly higher IL-2-Fc MFI values in IL-2-Fc+ CD4+ T-cells (boxed cells in d) relative to IL-2-Fc+ NK cells (n=2 mice, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test, P=0.0004). (f,g) Injected IL-2WTFc (f) and IL-2WTFcnil (g) proteins accumulate to higher levels on the surface of Tregs compared to any other analysed subset. Asterisks indicate significant differences relative to CD4+ IL-2-Fc+ Tregs, as determined by one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001). All data are displayed as mean±s.e.m. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.