Figure 2.
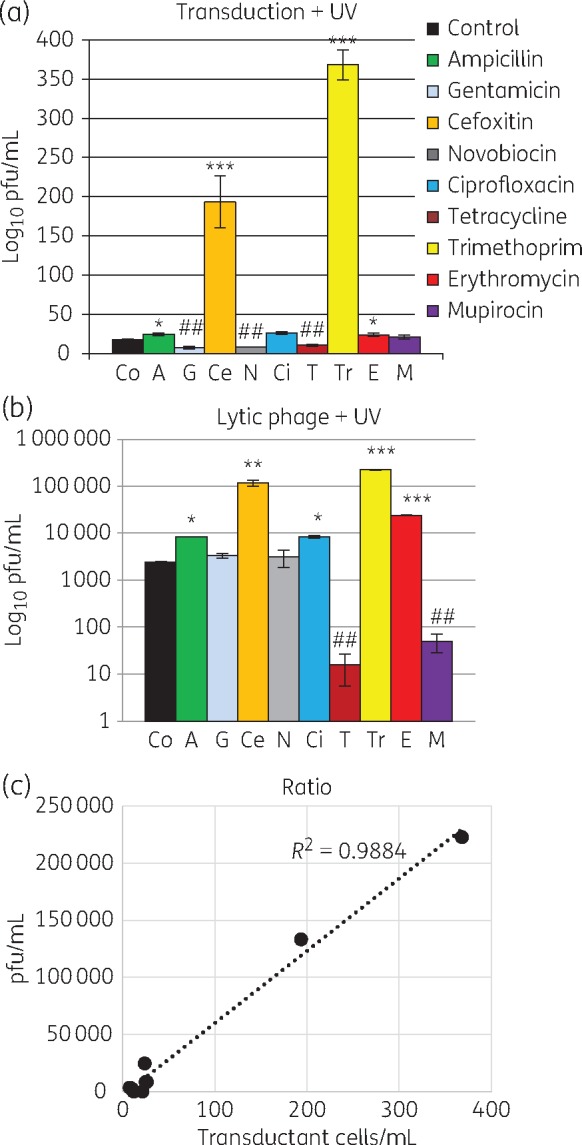
Sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics combined with UV light induce lytic and transducing particles in different ratios. (a) Transduction of ermC (using phage preparations treated with antibiotics and UV light) to recipient cells was significantly enhanced by cefoxitin and trimethoprim, and significantly lowered by gentamicin, novobiocin and tetracycline. (b) Lytic phage counted on RN4220 was higher than UV alone when exposed to cefoxitin and trimethoprim as well as ampicillin, ciprofloxacin and erythromycin. Lytic phage production was inhibited when exposed to tetracycline and mupirocin. (a and b) Mean of at least three experiments in triplicate (±SD). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, a double hash denotes reduction (##P < 0.01). (c) Correlation between transducing particles and lytic phage for each donor cell lysate was 0.99, indicating that under UV light stress, the ratio of transducing and lytic phage particle is not dependent on the antibiotic tested. This figure appears in colour in the online version of JAC and in black and white in the print version of JAC.
