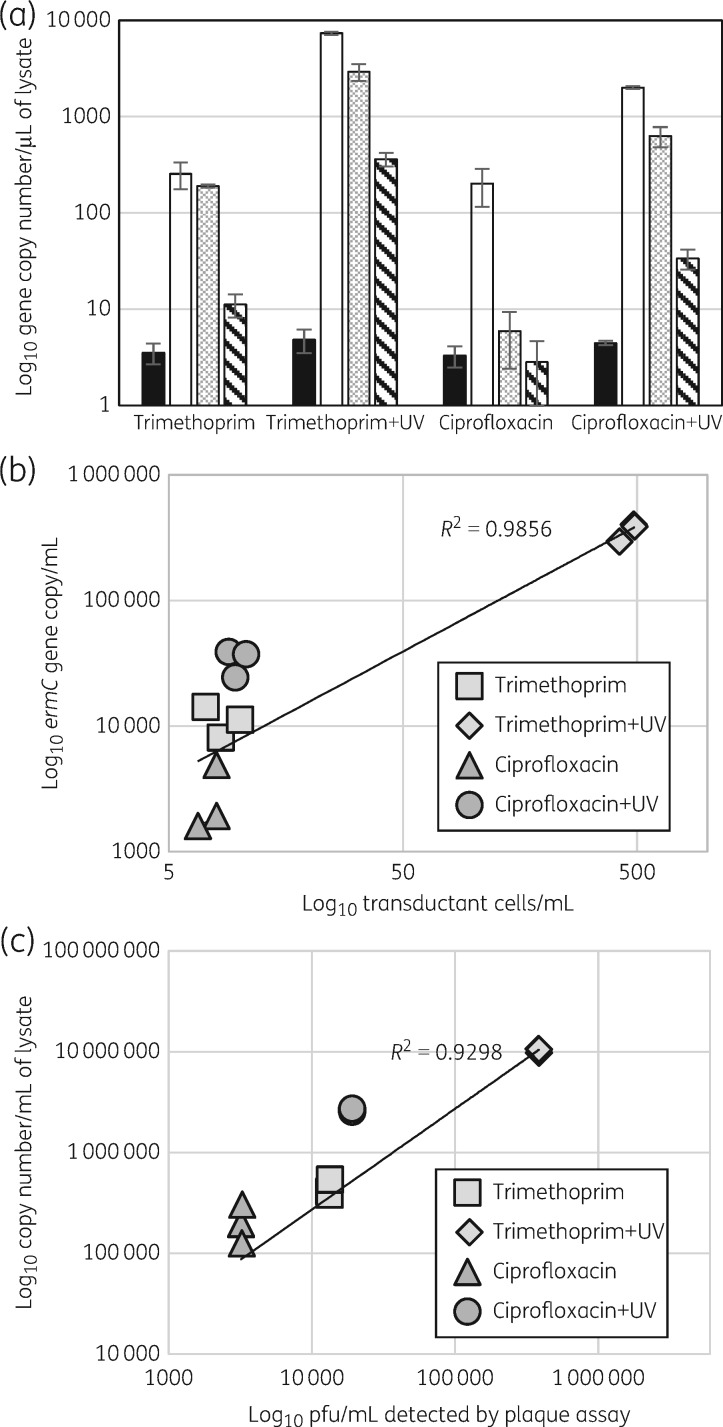
Figure 4.
Copy number of ermC and phage genes in phage particles correlates with transduction and lytic activity. (a) ddPCR was used to measure the copy number of the chromosomal gene nuc (black), phage genes represented by Φ1int (white) and Φ2int (grey patterned) and plasmid-borne ermC (hatched) in purified phage particles generated by exposure to trimethoprim or ciprofloxacin with or without UV light. ermC, Φ1 and Φ2 copy numbers were significantly different (P < 0.01) between all tested lysates apart from Φ1 exposed to ciprofloxacin and trimethoprim. The copy number of the nuc gene was significantly lower in comparison with ermC (P < 0.01) and phage genes (Φ1int and Φ2int) in all lysates (P < 0.001) and did not differ between lysates. Bars represent mean values of three experiments with three replicates (±SD). (b) Correlation between ermC concentration and transduction of erythromycin resistance. (c) Correlation between the concentration of Φ1int and Φ2int (summed) and lytic activity. Each point represents the mean of duplicate testing of three different lysates.