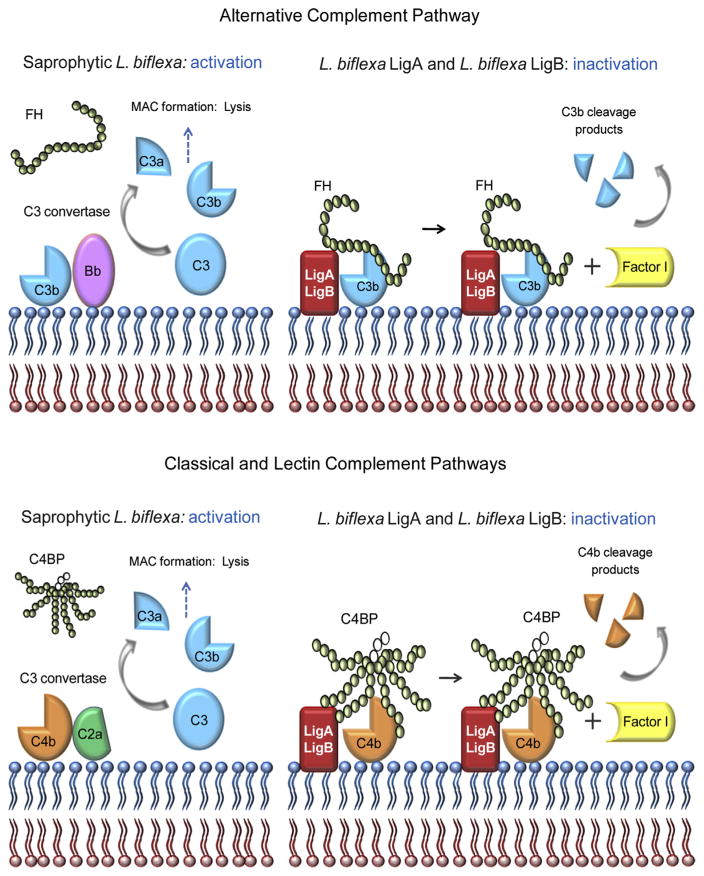
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of complement inactivation on the surface of L. biflexa expressing LigA or LigB. Saprophytic L. biflexa are susceptible to complement-mediated killing because they do not bind the host regulators FH and C4BP. In contrast, L. biflexa expressing LigA or LigB evade complement attack by acquiring these soluble regulators. Alternative pathway evasion is mediated by FH binding to LigA/LigB and the consequent C3b cleavage by FI, using bound FH as a co-factor. Classical and lectin pathways inactivation is achieved by C4BP binding to LigA/LigB, followed by FI-mediated cleavage of C4b. In the schematic representation of FH and C4BP, each circle represents one SCR domain. Open circles indicate the three SCR domains of the C4BP β-chain.