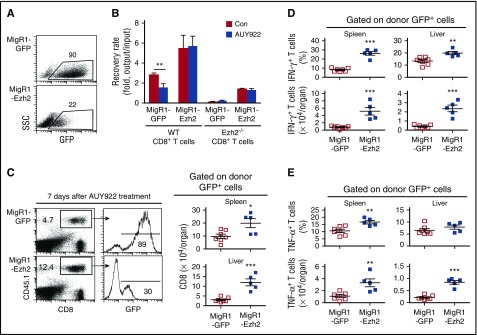
Figure 3.
AUY922 treatment reduces alloreactive T-cell response dependent on Ezh2. B6-derived CD8+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody (3 μg/mL), anti-CD28 antibody (2 μg/mL), and recombinant murine interleukin-2 (5 ng/mL). One day later, T cells were infected with retrovirus MigR1-GFP or MigR1-GFP–encoding Ezh2. (A) Dot plots show the fraction of GFP-expressing cells 4 days after culture. (B) The GFP+ cells were sorted and cultured for an additional 3 days in the presence or absence of AUY922. Cell recovery rate after culture was determined. (C-E) Retrovirally infected WT B6/SJL CD8+ T cells were transferred into unirradiated BDF1 mice, followed by AUY922 treatment on days 4, 5, and 6 after transplantation. On day 7, cells were recovered from recipient mice. (C) Dot plots and histograms show the fraction of donor T cells and GFP+ donor T cells, respectively. Graphs show the number of GFP+ donor T cells. (D) The fraction and number of IFN-γ–expressing GFP+ donor T cells. (E) The fraction and number of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)–expressing GFP+ donor T cells. Error bars indicate mean ± standard deviation. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001.