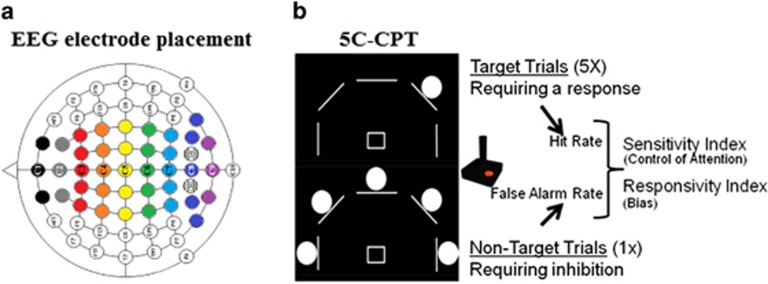
Figure 1.
Task schematics. Schematic of centroid mapping indicated by number, calculated according to weighted averages of neighboring channels as indicated by color (a). Five-choice continuous performance task (5C-CPT) schematic (b), where target trials are presented by a single circle (top), requiring a response from the joystick in that direction (up and left in the example provided), whereas non-target trials are presented by five circles (below), requiring the inhibition of responding. Target trials contribute to the hit rate (HR) measurement, whereas non-target trials contribute to the false alarm rate (FAR) measurement (response inhibition). These measures are combined to produce the primary outcome measure for control of attention, the SI, whereas responsivity index measures bias of responding.