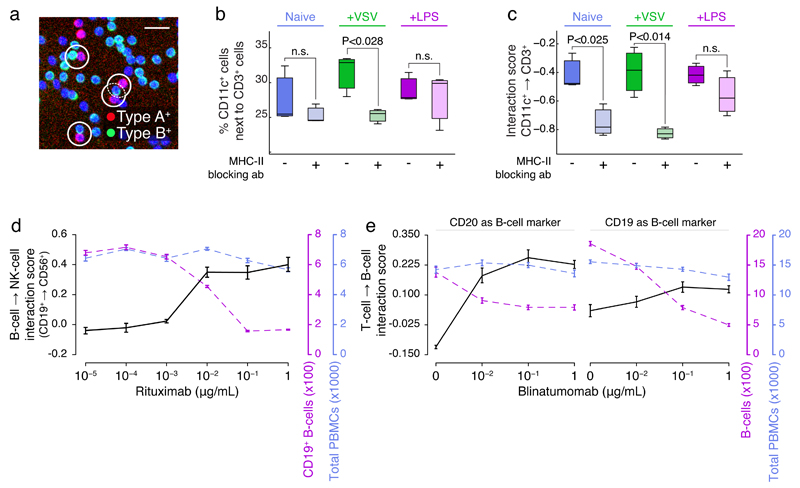
Fig 1. Quantifying PBMC cell-cell interactions perturbed by biologicals.
(a) Example 10x image of cell-cell PBMC subpopulation contacts, with selected contacts highlighted (white circles, scale bar is 25μm). (b) Percent of CD11c+ cells in contact with CD3+ cells, when naive or after stimulation with VSV or LPS, with or without pre-incubation with MHC-II blocking antibody. (c) CD11c+→CD3+ interaction scores corresponding to (d). Interaction score is calculated as the observed percentage of A cells in relation to B cells log2-relative to what is expected if data were randomized. (d) The interaction score of CD19+ B-cells→CD56+ NK cells (black axis; left), CD19+ B-cell counts (purple axis; right), or total PBMC counts (blue axis; far right) as function of increasing rituximab concentration. (e) Interaction scores of (left plot) CD3+ T-cells→CD19+ B-cells or (right plot) CD3+ T-cells→CD20+ B-cells (black axis; left), B-cell counts (purple axis; right), or total PBMC counts (blue axis; far right) as function of increasing blinatumomab concentration. (b-c) were performed in triplicate, and representative of three independent experiments; (d-e) were performed in at least 5 technical replicates, and are representative of (d) 5, or (e) 2 repeats over various healthy donors. Average and standard error of means, or boxplots, over technical repeats shown. A t-test was used to determine significance in (b-c).