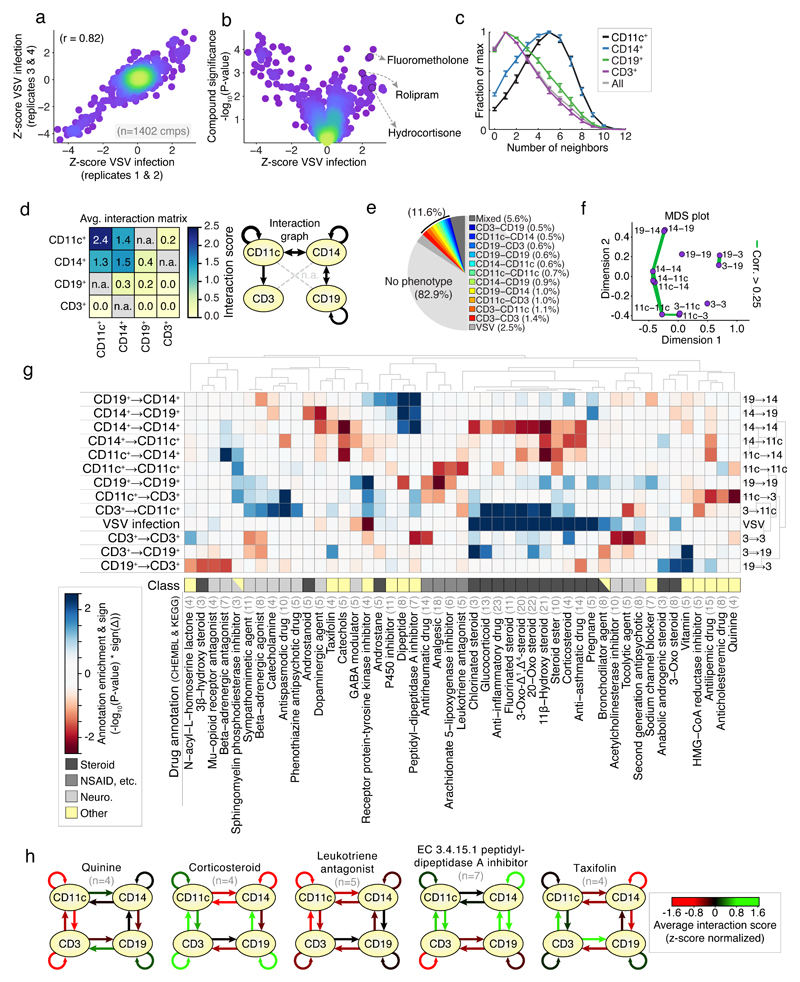
Fig 2. Screening for chemical modifiers of PBMC cell-cell contacts.
(a) reproducibility of VSV-infection over four replicates (average of two replicates per axis); dots correspond to compound; color indicates data density. (b) Average change in VSV infection per compound (z-score normalized) against the significance per compound (-log10(P-value)). Selected anti-inflammatory compounds shown. (c) Distributions of the number of direct contacts per cell type normalized to maximum; values aggregated over screen. (d) Left: Interaction scores of each pairwise combination averaged over screen; grey / n.a. indicates not measured; Right: visualization of the average interaction scores as interaction graph. (e) Percentage of compounds with unique or mixed phenotypes at 2-sigma significance. (f) MDS plot of the similarity between results over each measured interaction. Green lines connect interactions whose screening results are ≥ 0.25. (g) Hierarchical clustering of the enrichment (-log10(P-value) * sign of the phenotype) for selected top-enriched drug classes over all interactions measured, including VSV infection phenotype. Blue and red boxes indicate increased or decreased spatial phenotypes. Manual drug annotation class shown below. Light grey numbers indicate number of compounds. (h) Interaction graphs of average phenotypes for selected annotations from (g); red and green arrows indicate decreased or increased average interaction scores respectively (z-score normalized); black arrows indicate no change. (a-h) represent a large-scale screen performed in replicate or quadruplicate, at single-cell resolution, (13,152 cells per well for 7,680 wells). (a-b) measurements performed in quadruplicate. (c-f) summary statistics combined over 1,402 compounds (mean with standard error of mean shown (c)), (g-h) ≥ 3 compounds per compound annotation. (c-h) Represents 246,650,047 cell-cell interactions.