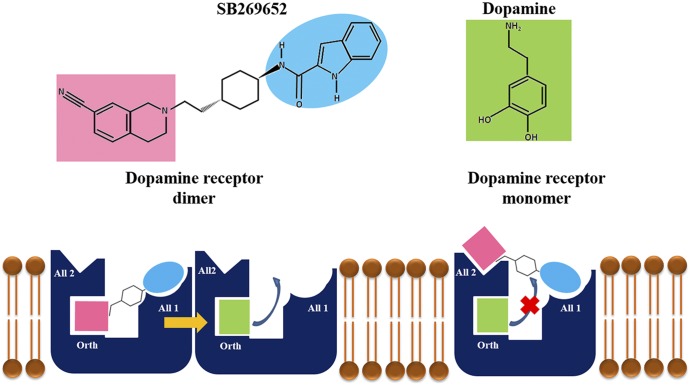
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the allosteric binding modes of SB269652 to dopamine receptor dimer and monomer. SB269652 is represented with its three main parts, the 7CN-THIQ group (pink), the trans-cyclohexylene spacer in the middle, and the indole-2-carboxamide tail (sky blue). In the left part of the image, SB269652 is shown bind in a bitopic mode to one protomer of the dopamine dimer, the 7CN-THIQ group to the orthosteric site (Orth), and the indole-2-carboxamide group to the allosteric site (All1), and exert an allosteric effect across dimer on dopamine sitting on the orthosteric site of the other protomer (Lane et al., 2014). In the right part of the image, SB269652 is shown bind to a dopamine-occupied monomer and prevent the dissociation of dopamine from the same receptor. In this configuration, the indole-2-carboxamide group would bind to the allosteric site as shown for SB269652 in the bitopic pose (All1), and the 7CN-THIQ group would engage an additional site on the extracellular part of the receptor (All2). This second arrangement of SB269652 on the dopamine-occupied receptor would be unfavorable in respect to the bitopic binding mode and would occur only for high doses of the drug.