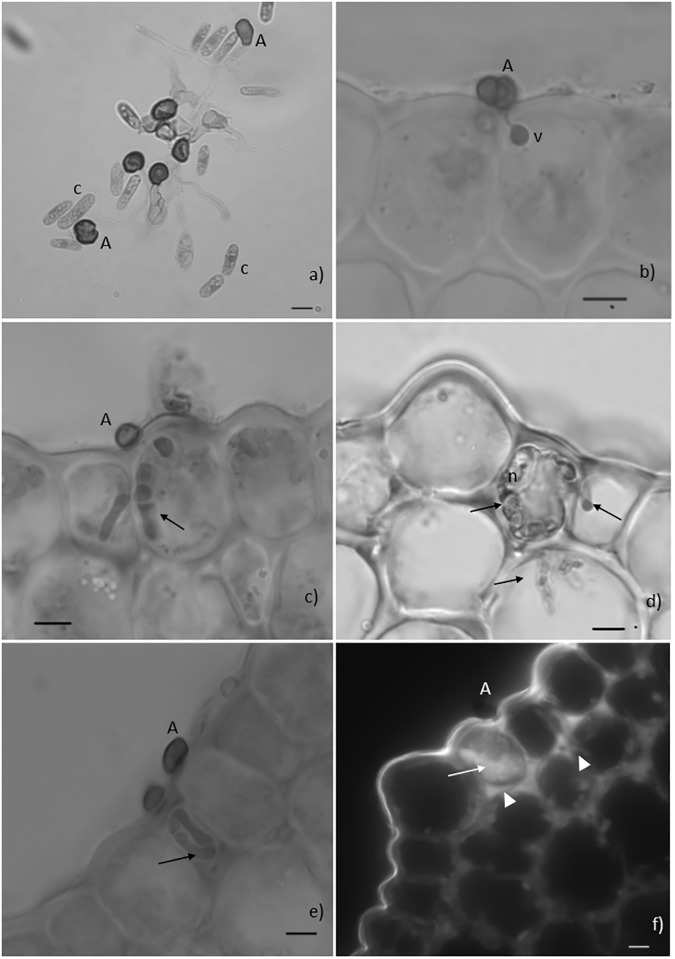
Fig 2. Fungal pre-and post-penetration growth stages and host responses.
Light microscope observations, cotton blue lactophenol staining (2a-2e) and epifluorescence test under blue light (2f). Fig 2a. Conidia (c) germination and formation of melanized appressoria (A) on the surface of a resistant hypocotyl, 24 hours post inoculation (hpi). Fig 2b. Infection site showing a melanized appressorium (A) and an infection vesicle (v) in the epidermal cell of the resistant hypocothyl, 48hpi. Fig 2c. Infection site showing a melanized appressorium (A) and hyphae inside two adjacent epidermal cells of the susceptible hypocotyl (arrow), 48hpi. Fig 2d. Fungal hyphae (arrows) in living and in necrotized (n) cells of the susceptible hypocotyl, 72hpi. Fig 2e. Infection site showing a melanized appressorium (A) and intracellular hyphae (arrow) confined to the epidermal cell of the resistant hypocotyl, 72hpi. Fig 2f. Infection site showing an appressorium (A) associated with autofluorescence of the cytoplasmic content of one epidermal cell (HR-like). Note that the walls of this cell and of adjacent epidermal and cortex cells are also autofluorescent (bars = 10μm).