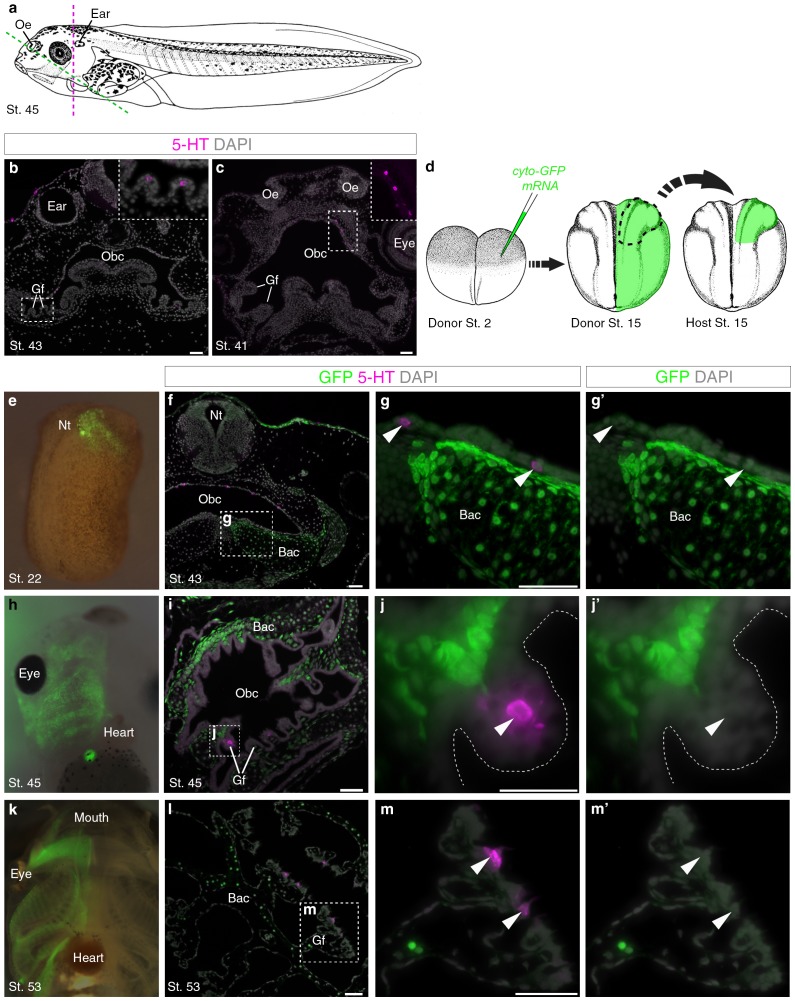
Figure 3. Putative Xenopus NECs are not neural crest-derived.
(a) Schematic of a stage 45 tadpole (Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1967). Dotted lines: section planes in b,f–g’ (magenta, transverse) and in c,i-j’,l-m’ (green, oblique). (b) Serotonergic cells in gill filament epithelium (putative NECs) are first detected at stage 43 (inset shows higher-power view). (c) Similar serotonergic cells are scattered in the orobranchial epithelium from stage 41 (inset shows higher-power view). (d) Schematic (modified from Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1967) showing neural crest labelling: GFP-donors, created by injecting cyto-GFP mRNA into one cell at the two-cell stage, were grown to stages 13–17, and neural folds grafted unilaterally to wild-type hosts. For grafted embryos grown to stage 53, donors were transgenic CMV-GFP embryos. (e) At stage 22, GFP labels neural crest cells migrating towards the branchial arches. (f–g’) At stage 43, GFP labels branchial arch cartilage and surrounding mesenchyme, but not putative NECs (arrowheads) in the orobranchial epithelium. (h–j’) At stage 45, GFP-positive neural crest cells are visible in the branchial arches (whole-mount and section from different embryos). GFP labels branchial arch cartilage and mesenchyme, but not putative NECs (arrowheads) in the gill filaments. (k–m’) At stage 53 (transgenic CMV-GFP donors; whole-mount and section from different embryos), GFP labels branchial arch cartilage and mesenchyme, but not putative NECs (arrowheads) in the gill filaments. 5-HT, serotonin; Bac, branchial arch cartilage; Gf, gill filament; Nt, neural tube; Obc, orobranchial cavity; Oe, olfactory epithelium. Scale-bar: 50 μm.