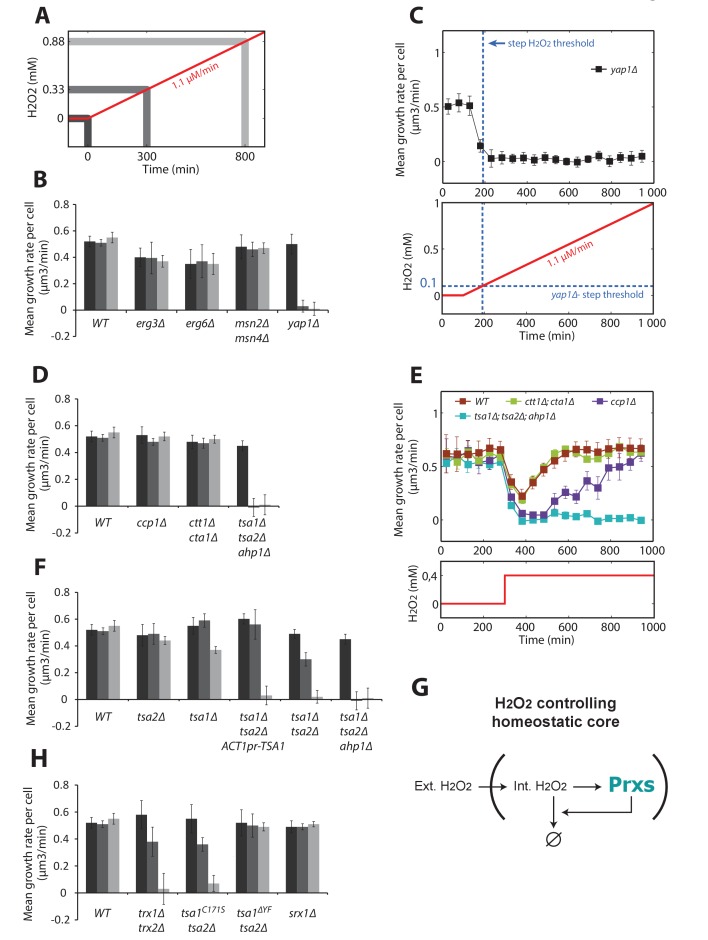
Figure 5. Genetic determinants of adaptation to ramped increases in H2O2.
Quantification of mean growth rate upon exposure to a linear ramp (δ = 1.1 μM/min) starting at t = 100 min in various genotypes. (A) Illustration of the H2O2 ramp experiment indicating the timing of the measurements. (B) Stress response and membrane permeability mutants. (C) Details of the ramp experiment in the Δyap1 mutant. The dashed blue lines indicate the adaptation threshold obtained in step experiments (Figure 1G). (D) Yap1 effectors mutants. (E) Step experiment performed with Yap1 effectors mutants exposed to 0.4 mM H2O2. (F) Prxs mutants. (G) Schematic of a negative feedback control showing the essential role of Prxs in the H2O2 homeostasis. (H) Mutants affecting the peroxidatic cycle of Prxs. Error bars are SEM (N > 100). See also Figure 5—figure supplement 1.