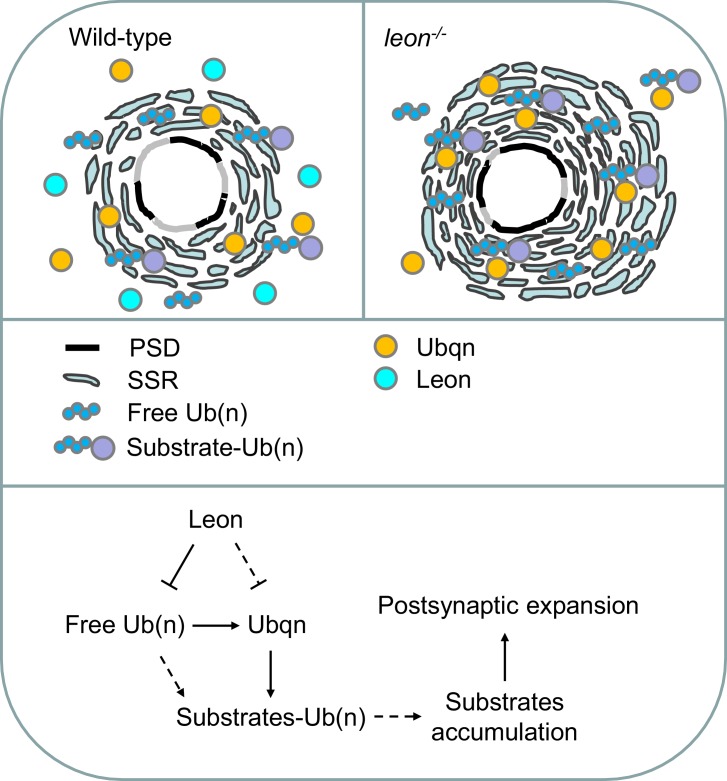
Figure 11. Model for Leon in maintaining postsynaptic ubiquitin homeostasis and protein degradation.
Schematics show postsynaptic distributions of free and substrate-conjugated ubiquitin chains in wild-type (upper left) and leon mutant (upper right) postsynaptic sites. (bottom) The proposed pathway for Leon/Usp5 in postsynapses: Leon downregulates the levels of free ubiquitin chains through the deubiquitinating activity. Accumulation of free ubiquitin chains promotes Ubqn elevation, and Leon may suppress Ubqn levels through alternative pathways (dotted lines). Accumulated Ubqn could bind and stabilize ubiquitinated substrates. However, free ubiquitin chains and Ubqn when both are increased, collaborate to induce more accumulations of ubiquitinated substrates. Finally, accumulated substrates contribute to postsynaptic protein accumulation and SSR and PSD expansions (Solid lines: supported by experiments in this study; dash lines: proposed links).