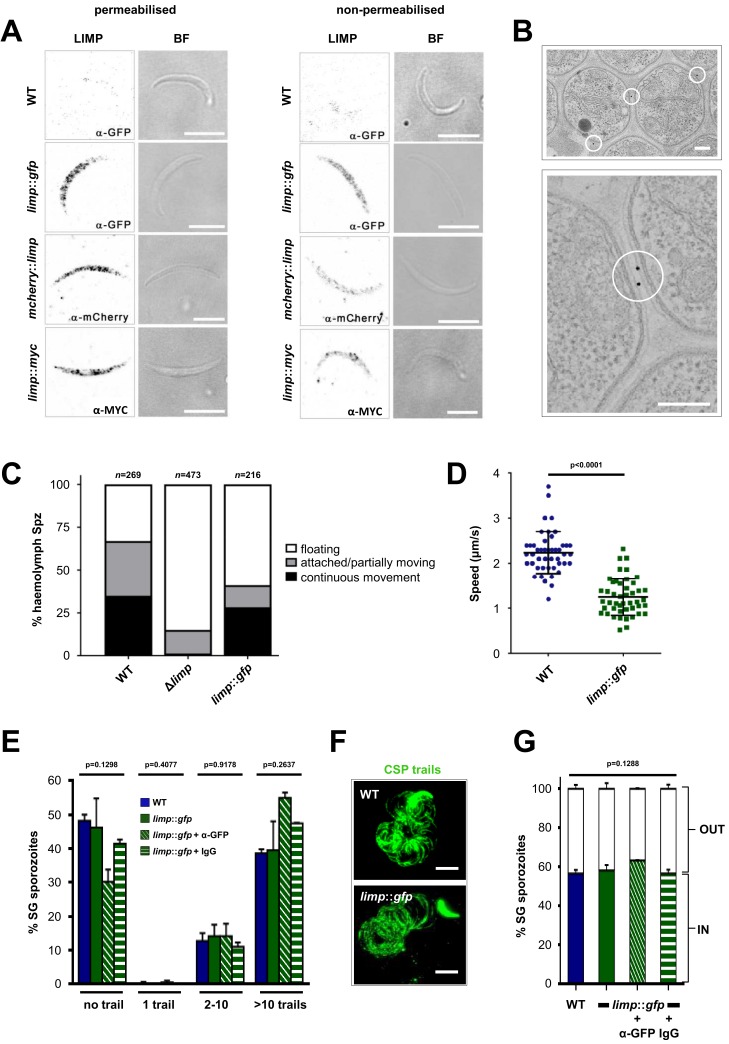
Figure 4. LIMP localises to the parasite plasma membrane but its function cannot be targeted by blocking antibodies.
(A) Immunofluorescence assays of WT, limp::gfp, mcherry::limp and limp::myc salivary gland sporozoites. Sporozoites were stained with anti-GFP (α-GFP), α-mCherry or α-MYC antibodies at days 17–20 p.i. BF=brightfield images. Scale bars = 5 µm. (B) Immuno-electron microscopy of limp::gfp salivary gland sporozoites with anti-GFP antibodies identifies LIMP::GFP (black dots inside white circles) at the parasite plasma membrane. Scale bars = 200 nm. (C) Live motility assay to investigate movement patterns of WT, Δlimp and limp::gfp haemolymph sporozoites (Spz). Most Δlimp sporozoites display a severe attachment phenotype and thus are incapable of moving. The indicated total number of sporozoites derived from three independent experiments in case of WT and six or two independent assays were performed for Δlimp or limp::gfp, respectively. (D) Moving limp::gfp haemolymph sporozoites show reduced gliding speed. Dot plots show means±SEM of 46 analysed sporozoites from three independent experiments per parasite line; p-value for Mann-Whitney test. (E) CSP shedding-based gliding motility assay of WT and limp::gfp salivary gland (SG) sporozoites in the presence and absence of anti-GFP (α-GFP) blocking antibodies or control IgGs. Bars show means±SEM. WT (one experiment; n = 3; 280 sporozoites analysed); limp::gfp (two independent experiments; n = 5; 492 sporozoites analysed); limp::gfp + α-GFP (one experiment; n = 3; 197 sporozoites analysed); limp::gfp + IgG (one experiment; n = 3; 234 sporozoites analysed). (F) Representative images of WT and limp::gfp (no antibody) CSP gliding trails. Scale bars = 10 µm. (G) WT and limp::gfp salivary gland (SG) sporozoite hepatocyte invasion assay in the presence and absence of anti-GFP (α-GFP) blocking antibodies or control IgGs. Bars show means±SEM of invading (IN) and non-invading (OUT) parasites. Data are from one experiment (n = 3) for all parasite lines and conditions. Numbers of sporozoites analysed: WT = 346, limp::gfp = 763, limp::gfp + α-GFP = 807, limp::gfp + IgG = 742. (E and G) p-values for Kruskal-Wallis test.