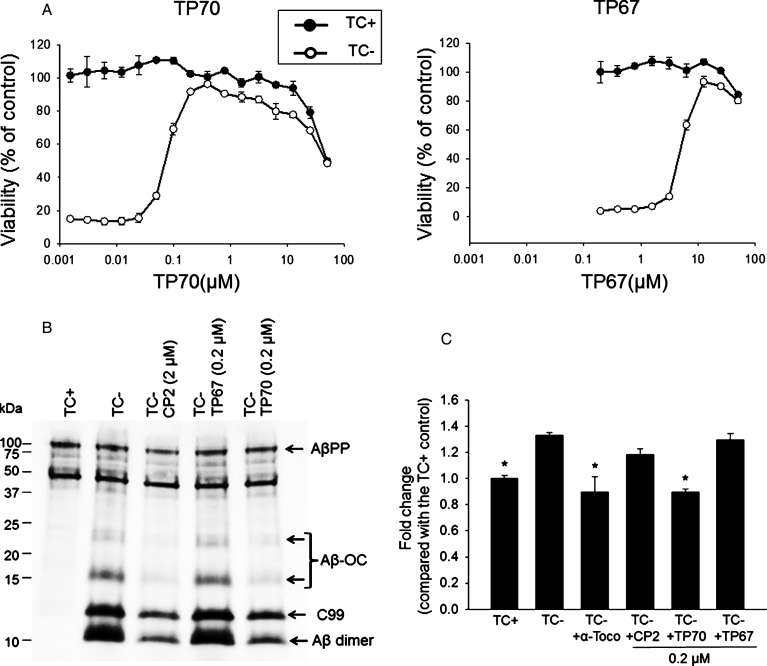
Fig.2.
The neuroprotective effects of TP70. A) MC65 cells were induced to express AβO by withdrawal of tetracycline (TC-) from the medium in the presence of indicated concentrations of TP70 or TP67. Cultures in the presence of TC (TC+) as well as the drug were used as controls to determine the toxicity of the drug independent of Aβ. At 72 h, viability was assessed by MTT assay. Data are expressed as mean percentage viability (n = 3) with parallel TC+ cultures without drug set at 100% viability. Error bars represent standard error. The EC50, TD50, and TI values of TP70 were calculated and listed in Fig. 1. B) MC65 cultures at 24 h after TC withdrawal were homogenized and 5 μg cellular proteins were subjected to Tris/tricine SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis with antibody 6E10 for Aβ1-16. The band pattern was comparable to our published data [8, 38]; accordingly, each band was identified. Both CP2 and TP70, but not TP67, reduced the levels of Aβ-OC, C99, and Aβ dimer without altering the level of AβPP. C) Fluorescence intensity of each culture conditions were expressed as fold change compared to the TC+ (no Aβ expression) condition. n = 7-8, *p < 0.05 compared to the TC- condition (with Aβ expression). TP70 and α-tocopherol but not CP2 or TP67 reduced ROS levels related to intracellular Aβ expression. Data are expressed as mean percentage viability (n 1/4 7) with parallel +TC cultures set at 100% viability. Error bars represent standard error.