Figure 4. Involvement of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in the effect of FLX.
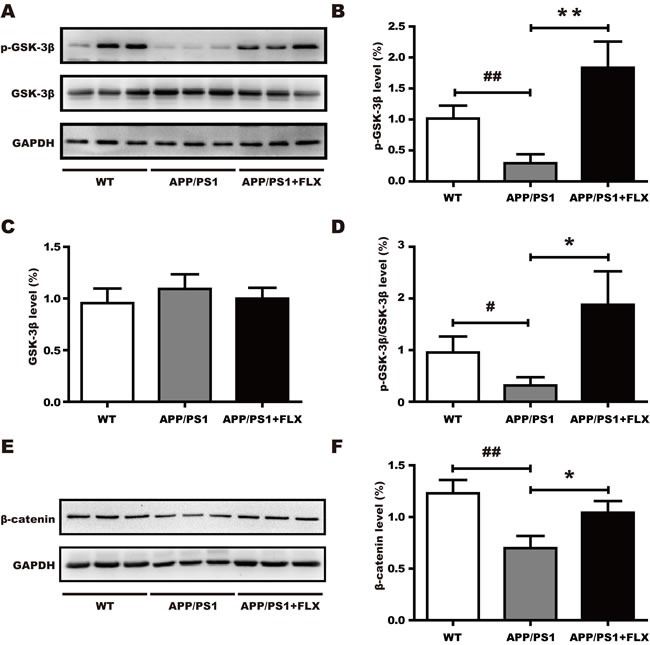
FLX increases the level of phosphorylated of GSK-3β and the level of β-catenin in middle-aged APP/PS1 mice. A. Western blots showing the expression levels of p-GSK-3β and total GSK-3β in FLX-treated middle-aged APP/PS1 mice. GAPDH was used as an internal control. B.-D. Quantification of the levels of GSK-3β and p-GSK-3β, along with the p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β ratio, in middle-aged APP/PS1 mice. B. The level of p-GSK-3β was significantly increased in the FLX-treated mice. C. There were no significant differences in the levels of total GSK-3β among the three groups. D. The p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β ratio was significantly increased in FLX-treated mice. E. Western blots showing the expression level of β-catenin in middle-aged APP/PS1 mice after FLX treatments. GAPDH was used as an internal control. F. Quantification of the level of β-catenin in middle-aged APP/PS1 mice. The level of total β-catenin was markedly increased after FLX treatment of middle-aged APP/PS1 mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. n = 5-6/group. ##, P < 0.01, vs. WT group. #, P < 0.05, vs. WT group. ** P < 0.01, vs. APP/PS1 group. *, P < 0.05, vs. APP/PS1 group.
