Figure 2. SRRM4 regulates RNA splicing of the MEAF6 gene.
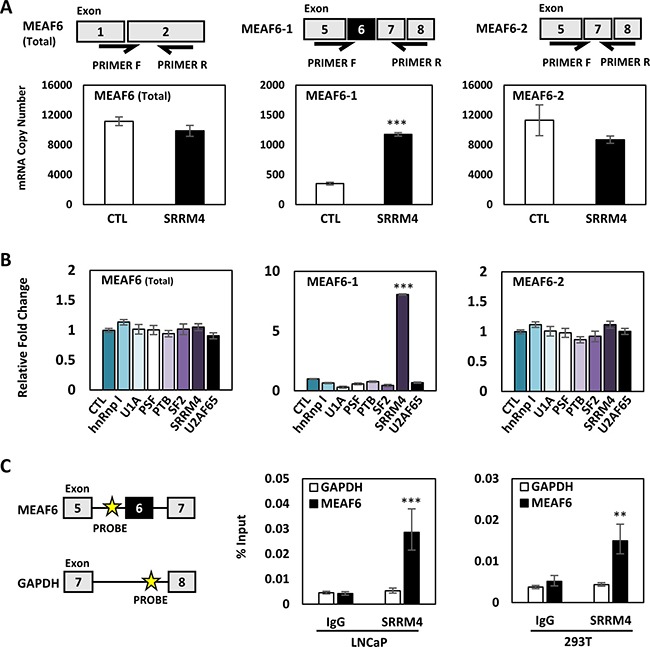
(A) Illustration of splice variant-specific primers designed to detected total MEAF6, MEAF6-1, and MEAF6-2 mRNA levels. LNCaP cells seeded in 6-well plates were transiently transfected with 4 ug of Flag-SRRM4 for 24 hours and were isolated for RNA. Real-time qPCR for absolute quantification of total MEAF6, MEAF6-1, and MEAF6-2 using a standard curve was performed. (B) LNCaP cells were transiently transfected with a panel of RNA splicing factors (hnRnp I, U1A, PSF, PTB, SF2, SRRM4, U2AF65). Cells were then extracted for RNA. Relative quantifications of total MEAF6, MEAF6-1, and MEAF6-2 were compared to 18S via real-time qPCR. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM (one-way ANOVA; n = 3; ***denotes p < 0.001). (C) RNA-ChIP was performed with 293T and LNCaP cells in 10 cm dishes. Cells were transfected with 10 ug of Flag-SRRM4 and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody following fixation with paraformaldehyde. Eluted RNA fragments were used as templates for real-time qPCR primers antisense for intron sequence upstream of alternatively spliced exon of MEAF6-1. Position of probes for MEAF6-1 and GAPDH is indicated by the yellow star. Otherwise indicated, results are presented as the mean ± SEM (Student t-test, n = 3 ***denotes p < 0.001 and **denotes p < 0.01).
