Figure 6. Effect of VP on HIPPO pathway genes of EMCA cells.
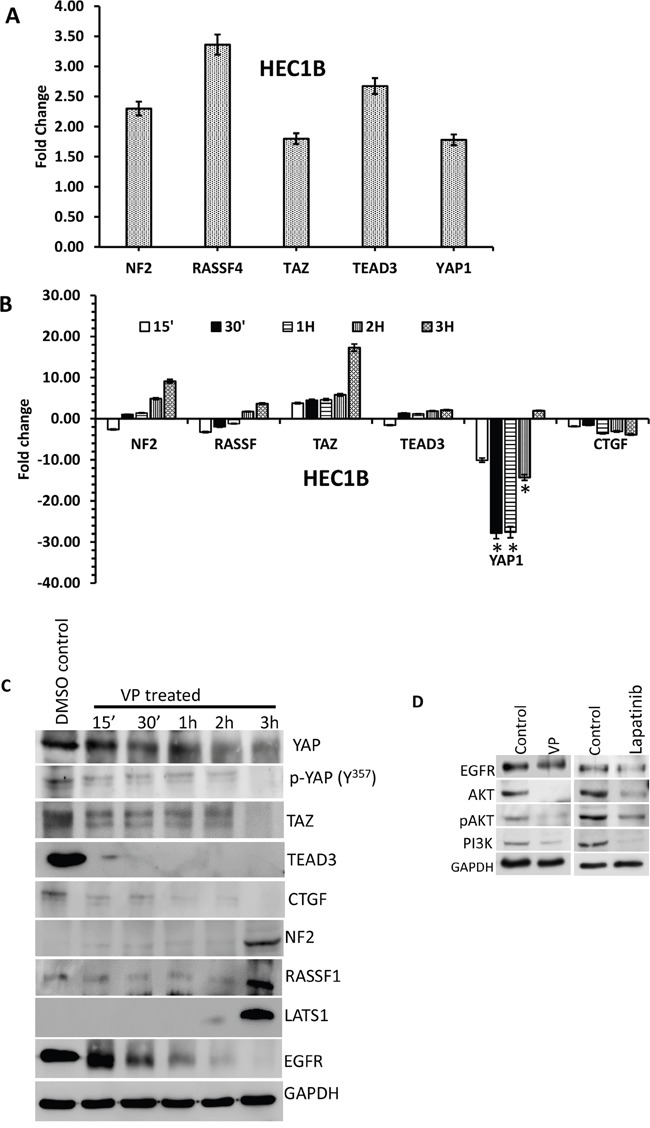
A. Effect of VP on HIPPO pathway of EMCA cells: cDNA RTPCR arrays were run after treatment of endometrial cancer cells with VP at 10 nM concentration for 3h. Control cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle). n=2 for each cell line and treatment. *Statistically significant at p<0.05. Error bars indicate Mean ±SEM. B. RTPCR analysis of selected HIPPO pathway genes. All the genes were normalized to the expression of GAPDH, β-actin, PGK1, LDHA and PPIH. *Statistically significant at p<0.05, by one-way ANOVA. DMSO control vs VP treated samples. Error bars indicate Mean ±SEM. p values are 0.0459, 0.0460 respectively. For each gene, duplicates were performed from 3 different samples for each treatment. n>6. C. Western blot time course of VP effect on YAP-mediated signaling molecules. Equal amounts of proteins (40μg) from untreated and treated (10 nM VP, 0 to 3 hrs.) EMCA cell lysates were loaded on 8% to 10% gels and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, which were then probed with respective antibodies. The westerns were run on separate blots. They were reprobed with GAPDH which was used a positive loading control. n=3. D. Western blots showing VP and Lapatinib effects on EGFR-mediated signaling molecules. Equal amounts of proteins (40μg) from untreated and treated (10 nM VP, 15 minutes; Lapatinib 20μM, 1h.) HEC-1-B cell lysates were loaded on 8% to 10% separate gels and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, which were then probed with respective antibodies. They were reprobed with GAPDH which was used a positive loading control. n=3.
