Figure 5. Z-LIG sensitizes TAM-resistant breast cancer cells in a caspase- independent manner.
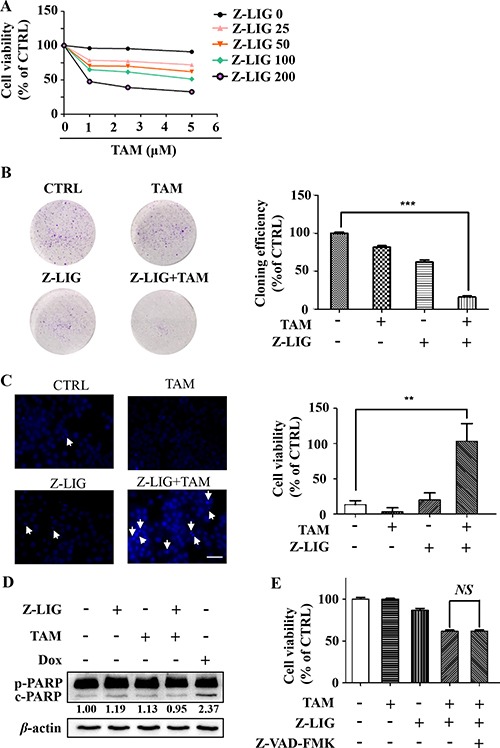
(A) Effect of combinatorial Z-LIG and TAM on cell viability. MCF-7TR5 cells were pretreated with Z-LIG as indicated for 12 h and then treated with TAM as indicated for 72 h. The cell viability was determined by SRB assay. (B) Effect of combinatorial Z-LIG and TAM on colony formation. MCF-7TR5 cells were pretreated with or without Z-LIG (50 μM) for 12 h, then treated with TAM (2.5 μM) and allowed to grow for 2 weeks before stained with 0.005% crystal violet. Adjacent picture depicts the crystal violet-stained colonies and bar graph indicated the cloning efficiency compared with untreated control. (C) MCF-7TR5 cells were pretreated with or without Z-LIG (50 μM) for 12 h and then exposed to TAM (5 μM) for 48 h. Morphologic change of apoptotic cells was evaluated by Hoechst 33342 staining and observed by fluorescence microscope (400×). Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) MCF-7TR5 cells were pretreated with or without Z-LIG (50 μM) for 12 h, and then were exposed to TAM (5 μM) or DOX (0.5 μM) as positive control. The expression of pro-PARP (p-PARP) and cleaved-PARP (c-PARP) were determined by Western blotting. The blots were a representative of three independent experiments. (E) MCF-7TR5 cells were pretreated with or without pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (25 μM) for 2 h and with or without Z-LIG (50, 200 μM) for 12 h, and then treated with TAM (5 μM). The cell viability was determined by SRB assay. Values represent mean ± SD. NS, non-significant. Values represent mean ± SD. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.
