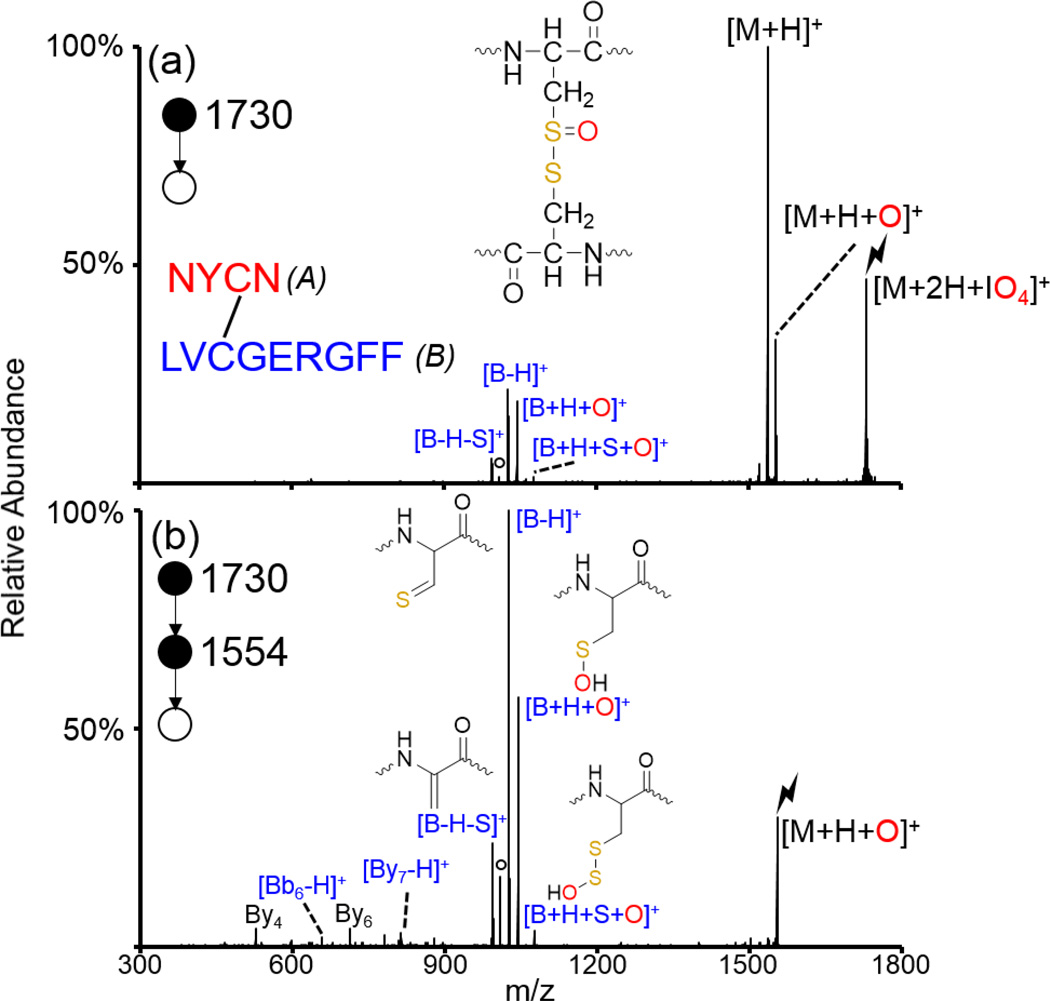
Figure 2.
Oxidation of an intermolecularly disulfide-linked peptide generated from a peptic digest of insulin. CID of (a) the ion/ion complex between doubly protonated NYCN/LVCGERGFF and IO4−, and (b) CID of the oxidized species. The sequence of the peptide is shown inset in (a) along with the structure of the [M+H+O]+ species. Structures of the [B+H+S+O]+, [B+H+O]+, [B-H]+, and [B-H-S]+ species are shown in (b). Fragments derived from cleavage of the disulfide bond are indicated in blue as all fragments observed correspond to fragments from the B-chain (indicated in blue in inset). Lightning bolts indicate species subjected to CID and degree signs indicate water losses.