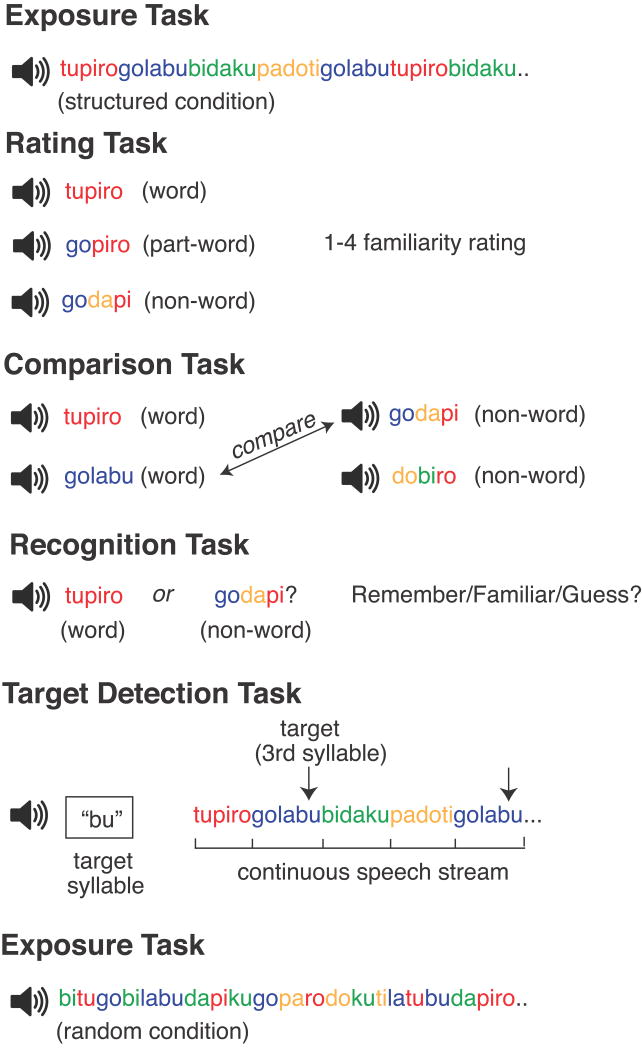
Figure 2.
Summary of experimental design. The exposure task in the structured condition consisted of 12 min of continuous auditory exposure to four repeating nonsense words. The exposure task in the random condition consisted of exposure to pseudorandomly repeating syllables. The main test of explicit memory was the rating task, which required participants to provide words and foil items with a familiarity rating. This task was followed by two additional tests of explicit memory, the comparison task and the recognition task. Finally, the target-detection task was a reaction-time-based measure of statistical learning, in which participants detected target syllables embedded in a continuous auditory speech stream composed of the four nonsense words. The syllable assigned as the target was rotated across trials.