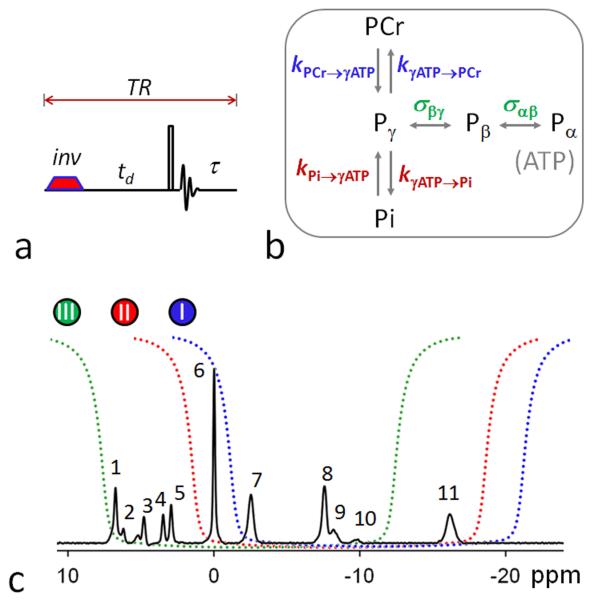
FIG. 1.
(a) The band inversion sequence consists of an adiabatic inversion pulse, followed by a varying delay td, a hard readout pulse and FID sampling and magnetization recovery period τ (≈ TR – td); (b) 31P magnetization exchange system in the human brain, showing various pathways that contribute to the magnetization transfer effects, including kinetic chemical exchange Pi → γ-ATP responsible for de novo ATP synthesis, kinetic chemical exchange PCr → γ-ATP catalyzed by creatine kinase (CK), and ATP intramolecular 31P-31P cross-relaxation γ-(α-) ↔ β-ATP, responsible for the nuclear Overhauser effect; and (c) the inversion profile of the three band inversion modules over a baseline-corrected brain 31P spectrum collected from the occipital lobe using pulse-acquire sequence with TR = 25 sec, NA = 6 and other common NMR parameters defined in Methods section (n = 6 subjects). Peak assignment: 1. Phosphoethanolamine (PE); 2. Phosphocholine (PC); 3. Intra- and extracellular inorganic phosphate (Pi); 4. Glycerolphophoethanolamine (GPE); 5. Glycerophosphocholine (GPC); 6. Phosphocreatine (PCr); 7, 8, 11. γ-, α-, and β-adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and 9. Nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD).