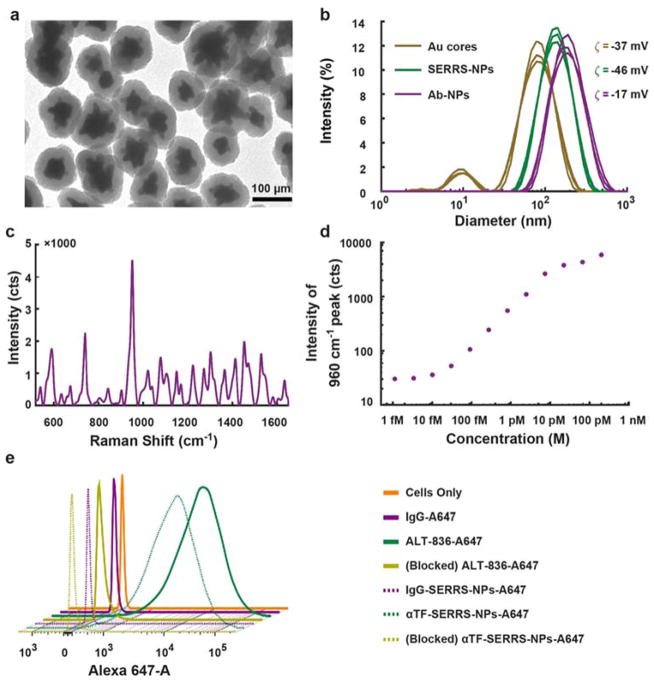
Figure 2. In vitro characterization of SERRS NPs.
(a) Transmission electron micrographs showing SERRS NPs, which have an average diameter of 70±24 nm for gold nanostar cores and 122±22 nm for final silicated NPs. (b) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) showing hydrodynamic diameter of 79, 141, and 164 nm with polydispersity index of 0.32, 0.17, and 0.20 and zeta potential (ζ) of −37.3±1.2 mV, −45.9±1.4 mV and −16.6±0.7 mV for gold cores, SERRS-NPs, and antibody conjugated SERRS-NPs, respectively. (c) SERRS spectrum showing characteristic peak at 960 cm−1 confirming the presence of Raman reporter molecule (IR 780 dye) in αTF-SERRS-NPs. (d) Limit of detection of SERRS NPs in solution was approx. 10 fM using conditions amenable to in vivo imaging. (e) Flow cytometry indicating no difference in TF binding affinity or specificity between αTF-A647 and αTF-SERRS-NPs-A647 in comparison to isotype and blocking controls.