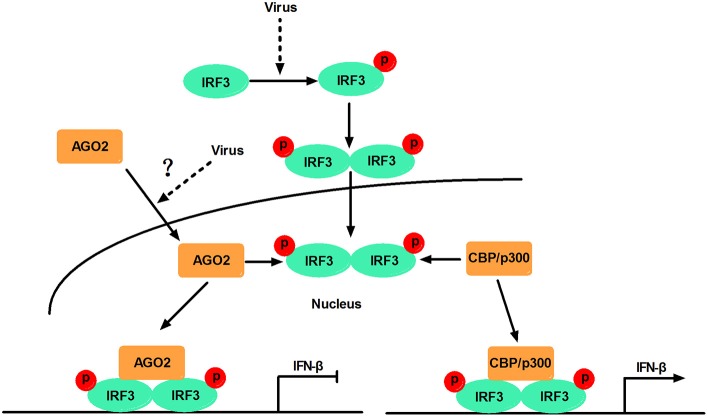
Figure 12.
Schematic diagram of AGO2 action on innate immune signaling pathway. Viral infection recruits kinases TBK-1 and IKKε to adaptor protein VISA and TRIF. These kinases phosphorylate IRF3, and phosphorylated IRF3 forms dimers that translocate into the nucleus and are activated. Activated IRF3 interacts with CBP/p300, which forms the transcription initiation complex, and induces production of IFN-β. However, AGO2 inhibits IFN-β promoter activation by interfering with IRF3–CBP interaction and represses formation of transcription initiation complex. H5N1 infection can reduce the distribution of AGO2 in the nucleus and further enhance IFN-β promoter activation.