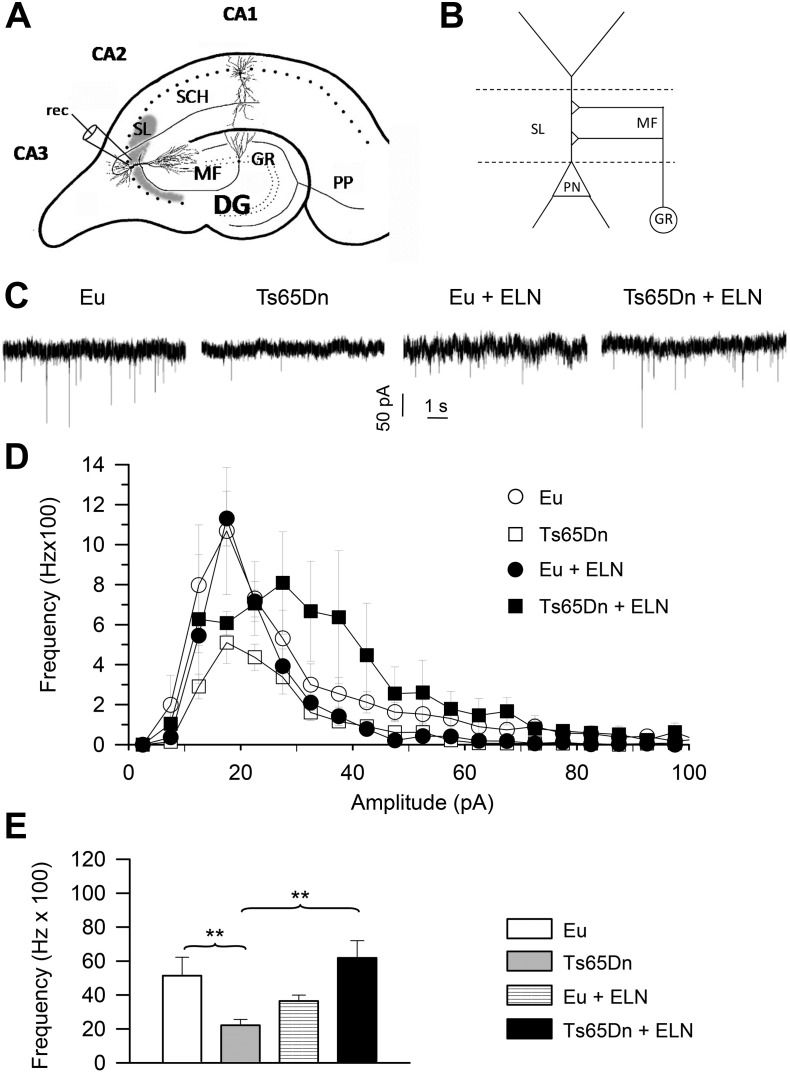
Fig. 7.
Long-term effect of treatment with ELN on mEPSC frequency in CA3 pyramidal neurons.
A: Schematic drawing of a section across the hippocampal formation showing the major intrinsic connections. Patch clamp recording (rec) of miniature synaptic potentials were carried out from pyramidal neurons of field CA3. The area occupied by the mossy fiber terminals in the stratum lucidum of field CA3 is indicated in gray. B: Mossy fiber circuitry in CA3. Mossy fibers establish excitatory synapses (+) with pyramidal neurons in the stratum lucidum of CA3. C: Exemplary current tracings recorded in the gap-free mode in four representative cells from untreated euploid and Ts65Dn mice and euploid and Ts65Dn mice treated with ELN, showing mEPSC activity. Holding potential was − 70 mV. Recordings were made in the presence of 1-μM TTx in the superfusing solution. D: Average frequency-distribution diagrams of mEPSC amplitude for untreated euploid and Ts65Dn mice and euploid and Ts65Dn mice treated with ELN. E: Average, overall mEPSC frequency in the four animal groups. Data derive from 9 untreated euploid mice (13 cells), 7 untreated Ts65Dn mice (18 cells), 8 ELN-treated euploid mice (15 cells), and 4 ELN-treated Ts65Dn mice (12 cells). Values in D-E represent mean ± SE **p < 0.01 (Linear mixed model analysis). Abbreviations: CA1–3, hippocampal fields; DG, dentate gyrus; ELN, ELND006; Eu, Euploid; GR, granule cell layer; MF, mossy fibers; PN, pyramidal neuron; PP, perforant pathway; PYR, pyramidal layer; SCH, Shaffer collaterals; SL, stratum lucidum.