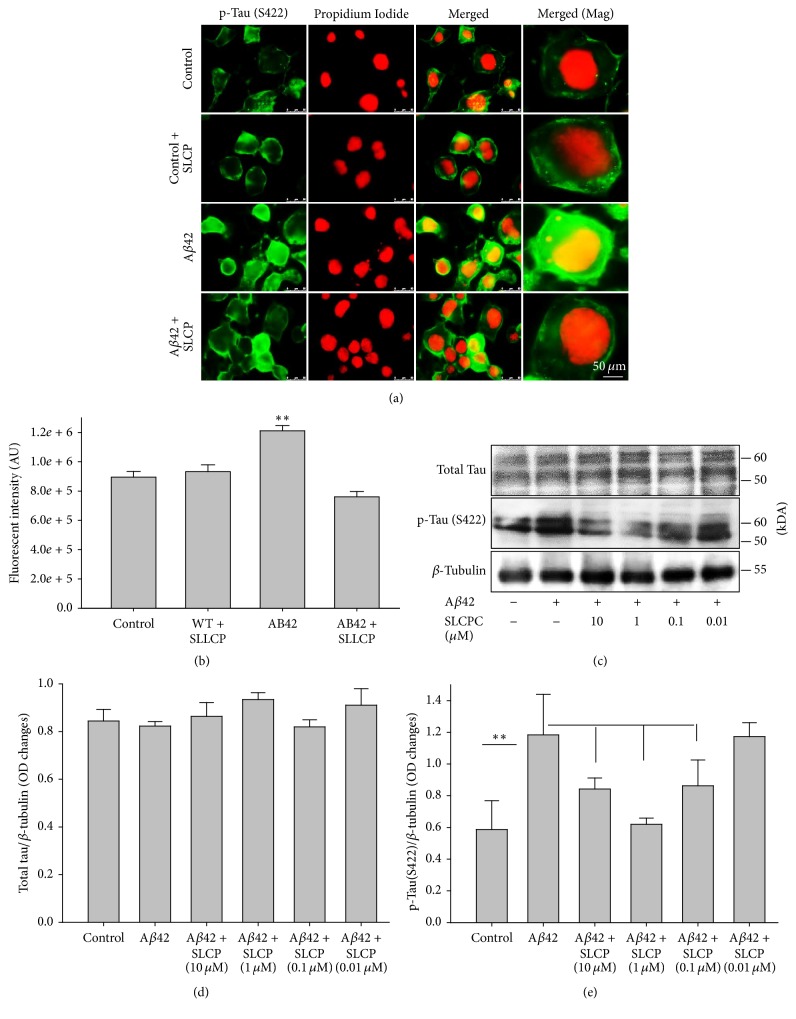
Figure 6.
Aβ42-induced p-tau was decreased by SLCP treatment. (a-b) N2a cells were treated with Aβ42 (10 μM) for 24 h in absence or presence of different concentrations of SLCP. The p-tau immunofluorescent signal was significantly increased after Aβ42 exposure (∗∗p < 0.01 relative to control) and normalized by SLCP (1 μM) treatment. Scale bar indicates 50 μm and is applicable to all other images. (c–e) Western blot data showed that p-tau (S422) was significantly increased by Aβ42 exposure, whereas SLCP treatment protected against such increase at 10, 1, and 0.1 μM levels (∗∗p < 0.01, in comparison to all other groups with different concentrations of SLCP treatment, except those given 0.01 μM).