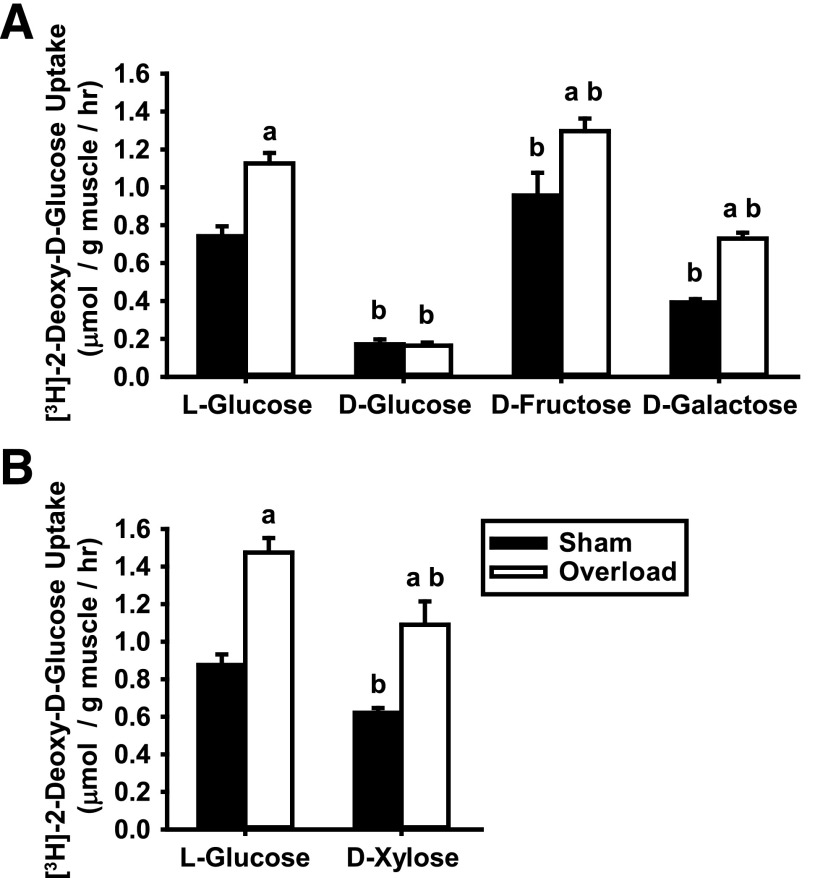
Figure 3.
Overload-induced increases in skeletal muscle glucose uptake involve a GLUT that can transport d-glucose, d-galactose, and d-xylose but not l-glucose or d-fructose. WT CD-1 female mice (6–8 weeks of age) underwent unilateral synergist ablation surgery to induce plantaris muscle hypertrophy. After 5 days, muscles were excised and preincubated in KRBB for 90 min, and [3H]-2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake was assessed ex vivo for 10 min in the presence of different hexoses as follows: 35 mmol/L l-glucose, d-glucose, d-fructose, and d-galactose (A) or 35 mmol/L l-glucose or d-xylose (B). Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 and denoted as follows: a, vs. sham; b, vs. l-glucose. N = 4–6 muscles/group.