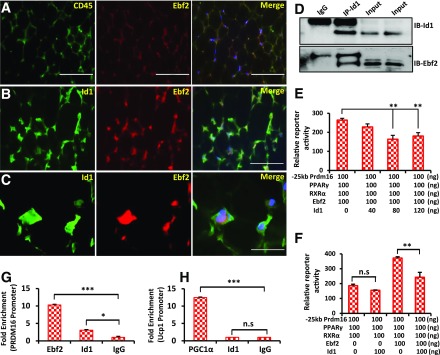
Figure 8.
Id1 suppresses Ebf2 transcriptional activity. A–C: Immunofluorescence staining showing the localization patterns of CD45/Ebf2 and Id1/Ebf2 in the iWAT of 2-month-old wild-type mice. Scale bars = 100 μm (A and B) and 20 μm (C). D: Co-IP followed by Western blot showing a direct interaction between Id1 and Ebf2. Input: 2% of IP reaction. E: Relative reporter activity of Prdm16 promoter–driven luciferase activity in the presence of PPARγ, RXRα (PPARγ binding partner), Ebf2, and different concentrations of Id1 plasmid (n = 2). F: Relative reporter activity of Prdm16 promoter–driven luciferase activity in the presence of PPARγ and RXRα and in the presence and absence of Ebf2 and Id1 (n = 2). Id1 suppressed Prdm16 promoter–driven luciferase activity only when Ebf2 was present. G and H: Chromatin IP-qPCR analysis of Ebf2 and Id1 binding to the Prdm16 promoter (G) and PGC1α and Id1 binding to the Ucp1 promoter (H) in day 4 differentiated HIB1B cells after normalizing to 18S DNA binding (n = 2). Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005. IB, immunoblot; kb, kilobase; n.s, not significant.