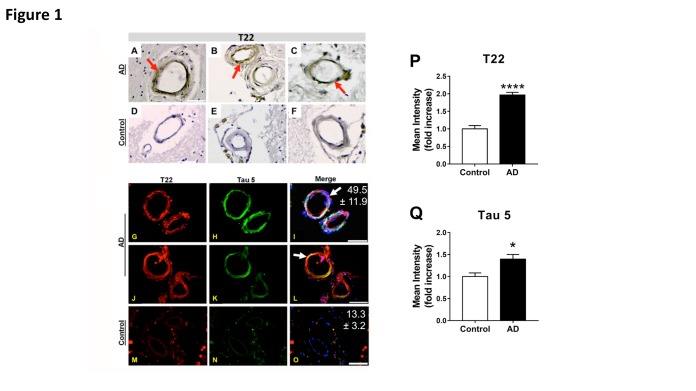
Figure 1. Deposition of tau oligomers in cerebrovasculature of human Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) brains.
(A-F) Representative images of immunohistochemistry studies using an oligomeric tau-specific antibody (T22) in cortical sections from AD (A-C) and age-matched controls (D-F). (G-O) Representative images of oligomeric tau (T22, red), and total tau (tau 5, green) cerebrovascular immunoreactivity in cortical sections of AD (G-L) and age-matched control (M-O) brains. Quantitative analyses of mean fluorescence intensity show increased tau oligomer- (T22, P) and total tau-specific (Tau5, Q) immunoreactivity in vasculature of AD brains compared to age-matched controls [****, t (28) = 8.12, p < 0.0001, and *, t(17) = 2.39, p = 0.029, for T22 and tau5 immunoreactivity respectively]. Our tau oligomer antibody T22 [18, 41] has been validated by immunoblot, ELISA, coimmunoprecipitation as well as rodent and human tissue staining, is produced endotoxin-free, and is commercially available (Millipore ABN454). For all studies, n=3 brains/group; 10-15 sections from each sample were analyzed for tau oligomers. All AD samples were tested and were positive for tau oligomers. Merged images are shown with DAPI (blue). In all panels, arrows indicate tau inclusions. Mean percent colocalization ± SEM of T22 with Tau 5 is reported in the figure. Scale bar 50 µm.