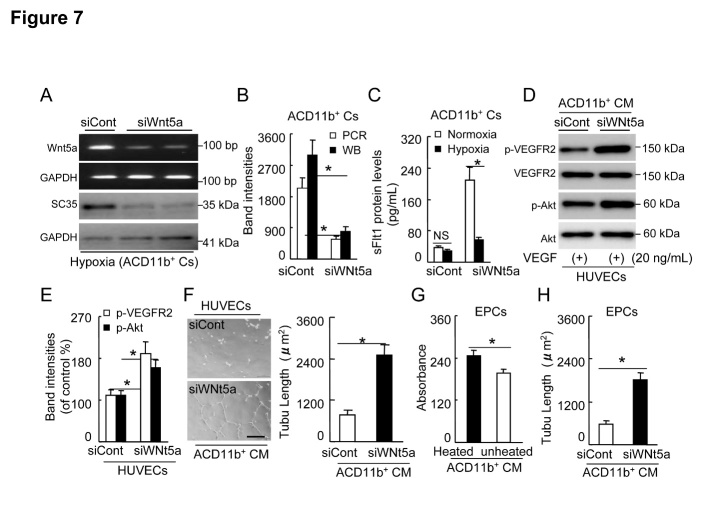
Figure 7. siWnt5a reduced the levels of Wnt5a mRNA and protein in aged mouse BM-derived ACD11b+Cs.
A and B) Subconfluent ACD11b+Cs were cultured (six-well-plates) in serum-free RPMI medium 1640 in presence of the siCont or siWnt5a under hypoxic condition for 24 hr, respectively, and the lysates were then subjected to the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the Western blotting (WB) assays. Representative PCR and immunoblots and combined quantitative data showed that siWnt5a decreased its mRNA and down-stream SC35 protein expression (n=3). C: Subconfluent ACD11b+Cs were cultured (six-well-plates) as the same conditions for 48 hr, respectively, and the conditioned media were then subjected to the ELISA with sFlt1 kits. The ELISA show that siWnt5a inhibited sFlt1 production in cultured ACD11b+Cs under hypoxia (n=8). D and E) Following collection of the culture medium of ACD11b+Cs treated as the same as above, the special fraction containing an approx. >70 kDa protein was isolated with 150 K and then 50 K AmiconUltra contricons, and we adjusted the protein concentration to 1.5 mg/ml for the cellular experiments. Representative immunoblots and combined quantitative data exhibit that siWnt5a-conditioned concentrated ACD11b+CM treatment (30 min) enhanced the enhancements of the VEGF-induced phospho-VEGFR2 (p-VEGFR2) and p-Akt as compared with siCont treatment in cultured HUEVCs (n=3). F) Representative images and combined quantitative data show that siWnt5a-conditioned ACD11b+CM ameliorated VEGF-induced HUVEC tubulogenic action as compared with control (n=6). G: As compared with unheated ACD11b+CM, unheated siWnt5a-conditioned ACD11b+CM exhibited an improvement of VEGF-induced young EPC-like c-Kit+ cell proliferation (n=7). H) siWnt5a-conditioned concentrated ACD11b+CM improved EPC-like c-Kit+ cell tubulogenesis (n=5). Data are mean ± SEM. *P<0.01 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc tests. NS indicates no significant. Scale bar, 50 μm.