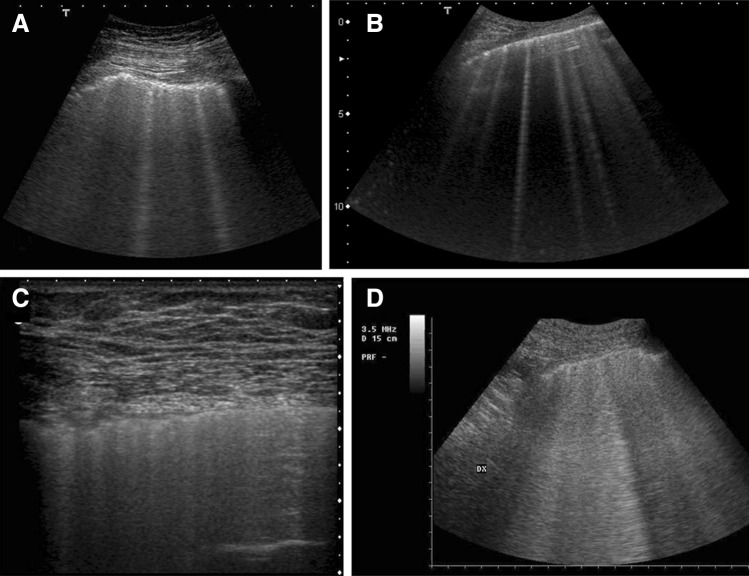
Fig. 3.
Morphological variations of the B-lines in sonographic interstitial syndrome. a Pneumogenic interstitial syndrome (pulmonary silicosis), 6 MHz convex probe. Irregular pleural line and multiple blurred, uneven B-lines. b Acute interstitial cardiogenic pulmonary edema. 6 MHz convex probe. The pleural line is regular. Some bright, laser-like B-lines with septal disposition are represented. c ARDS, non-gravitational area without consolidation. 7 MHz linear probe. On the right of the picture, an area of near-normal lung showing A-lines with a relatively regular pleura is visible. On the left of the image, the pleura is irregular, coalescent B-lines are hidden, and there is not a normal A-line pattern. d Non-consolidative ARDS: 6-MHz convex probe. Inhomogeneous white lung. The detection of single B-lines that appear laser-like is unusual. This pattern is consistent with non-consolidative alveolar flooding