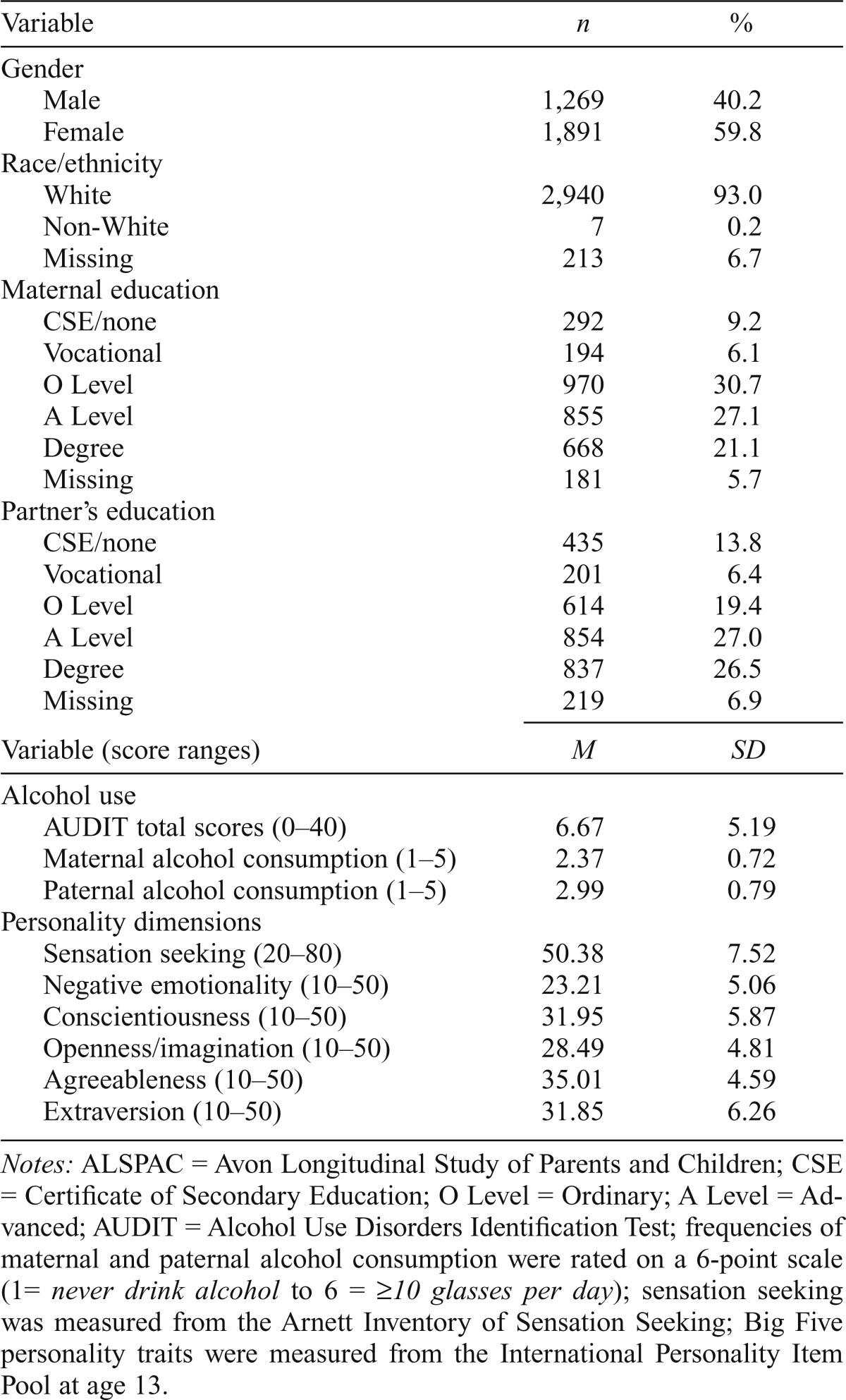
Table 1.
Frequencies, proportions, means, and standard deviations (SD) of study variables in ALSPAC (n = 3,160)
| Variable | n | % |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 1,269 | 40.2 |
| Female | 1,891 | 59.8 |
| Race/ethnicity | ||
| White | 2,940 | 93.0 |
| Non-White | 7 | 0.2 |
| Missing | 213 | 6.7 |
| Maternal education | ||
| CSE/none | 292 | 9.2 |
| Vocational | 194 | 6.1 |
| O Level | 970 | 30.7 |
| A Level | 855 | 27.1 |
| Degree | 668 | 21.1 |
| Missing | 181 | 5.7 |
| Partner’s education | ||
| CSE/none | 435 | 13.8 |
| Vocational | 201 | 6.4 |
| O Level | 614 | 19.4 |
| A Level | 854 | 27.0 |
| Degree | 837 | 26.5 |
| Missing | 219 | 6.9 |
| Variable (score ranges) | M | SD |
| Alcohol use | ||
| AUDIT total scores (0–40) | 6.67 | 5.19 |
| Maternal alcohol consumption (1–5) | 2.37 | 0.72 |
| Paternal alcohol consumption (1–5) | 2.99 | 0.79 |
| Personality dimensions | ||
| Sensation seeking (20–80) | 50.38 | 7.52 |
| Negative emotionality (10–50) | 23.21 | 5.06 |
| Conscientiousness (10–50) | 31.95 | 5.87 |
| Openness/imagination (10–50) | 28.49 | 4.81 |
| Agreeableness (10–50) | 35.01 | 4.59 |
| Extraversion (10–50) | 31.85 | 6.26 |
Notes: ALSPAC = Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children; CSE = Certificate of Secondary Education; O Level = Ordinary; A Level = Advanced; AUDIT = Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test; frequencies of maternal and paternal alcohol consumption were rated on a 6-point scale (1= never drink alcohol to 6 = ≥10 glasses per day); sensation seeking was measured from the Arnett Inventory of Sensation Seeking; Big Five personality traits were measured from the International Personality Item Pool at age 13.