Figure 2.
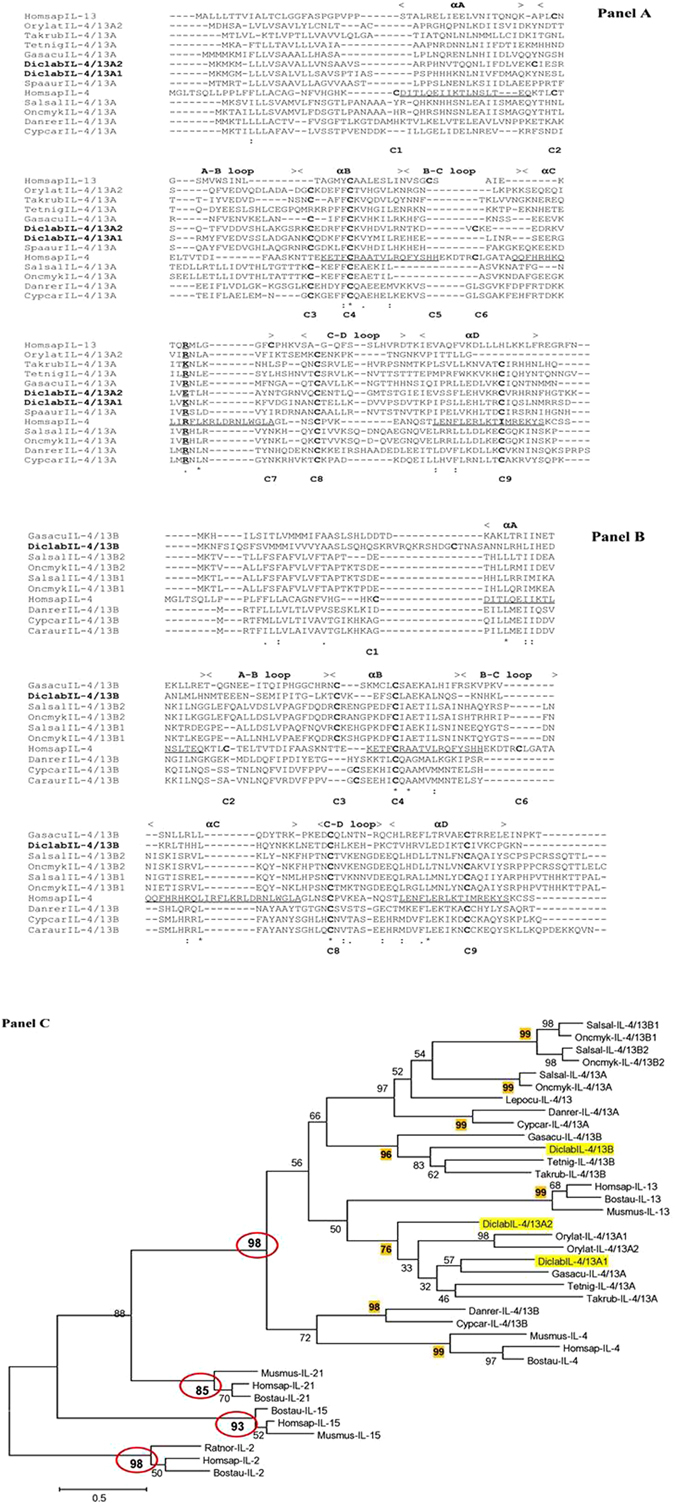
Panel A and Panel B. Amino acid sequence alignment of the predicted sea bass IL-4/13 isoforms with selected IL-4/13 molecules. The conserved amino acids are indicated with an “*” below the sequences, while “.” and “:” show amino acids with conserved physical and/or chemical properties. The position of the nine cysteine residues found in the different sequences is highlighted below the alignment and shown in bold along the sequences. The four α-helices and loop regions known for human IL-4 are shown above the alignment and the amino acids involved in the α-helices underlined in the human IL-4 sequence. Panel C. Phylogenetic tree analysis of fish IL-4/13 molecules with mammalian IL-4/IL-13 molecules and other closely related γ-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-15 and IL-21. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using amino acid multiple alignments and the neighbour-joining method within the MEGA7 program. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (10,000 replicates) was shown next to the branches. Lepisosteus oculatus (spotted gar) IL-4/13 was predicted from chromosome LG6. The bootstrapping values that support lineage-specific groupings are highlighted with a yellow background.
