Figure 1.
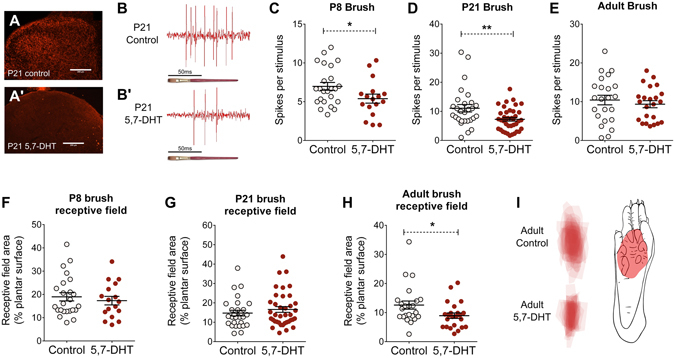
Serotonergic facilitation of dorsal horn neuron brush-evoked activity in young and adult rats. Hindpaw brush-evoked extracellular recordings of wide dynamic range (WDR) neurons were performed in laminae IV-VI of the lumbar spinal dorsal horn at P8, P21 and in adult P45 rats. 5-HT transporter (5-HTT) serotonergic terminals (red) were present in the dorsal horn of saline injected animals (A), but not in animals treated with 5,7-DHT (A′). Scale bar = 200 μm. Typical brush-evoked dorsal horn neuron spikes in P21 control rats (B) and 5,7-DHT treated rats (B′). Brush-evoked firing activity was lower in 5,7-DHT-treated animals at P8 (C) and P21 (D), but not in adult rats (E). Brush receptive field area was smaller than controls in 5,7-DHT-treated adults (H), but not at P8 (F) or P21 (G). Receptive fields of dorsal horn neurons in control and 5,7-DHT-treated adult groups were overlaid and mapped onto a standardised paw template to create a heat map for each group (I). A typical dorsal horn neuron brush receptive field from an adult control rat is shown for scale Bars indicate mean ± SEM. *,**P < 0.05, 0.01.
