FIGURE 1.
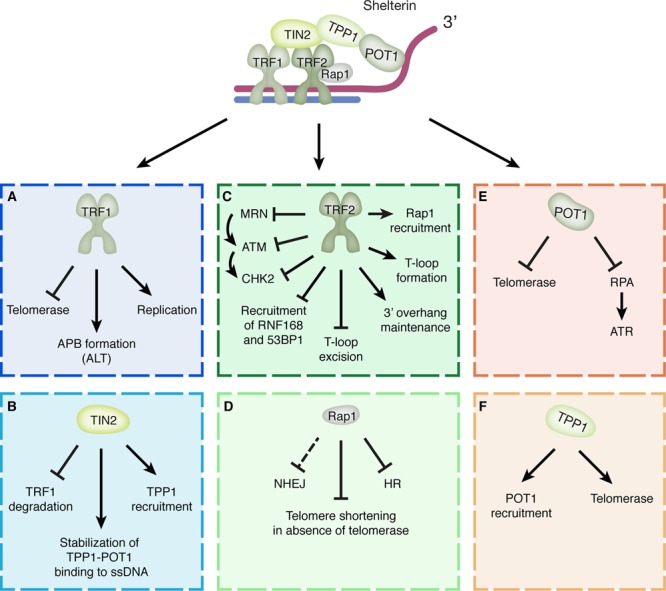
Shelterin components and their functions in telomere protection. (A) TRF1 facilitates telomere replication, restricts telomerase access and promotes the formation of APBs associated with ALT. (B) TIN2 recruits TPP1 to telomeres, stabilizes TPP1-POT1 binding to the ssDNA and prevents proteasomal degradation of TRF1. (C) TRF2 is involved in T-loop formation and stabilization, prevents T-loop excision, promotes maintenance of the 3′-overhang, recruits RAP1 to telomeres and prevents the recruitment of RNF168 and 53BP1. Furthermore, TRF2 interferes with ATM signaling by (1) preventing binding of the MRN complex and thereby activation of ATM, (2) binding ATM and interfering with its activation directly and (3) interacting with CHK2 and interfering with its phosphorylation. (D) RAP1 inhibits HR at telomeres and prevents telomere shortening in the absence of telomerase. In addition, RAP1 appears able to provide a back-up mechanism for inhibition of NHEJ when TRF2 function is impaired. (E) POT1 inhibits RPA binding and access of telomerase to the telomere single-stranded 3′-overhang. (F) TPP1 recruits POT1 to telomeres and stimulates the recruitment and activity of telomerase.
